Traditional Ginseng Extract extraction methods typically involve using water or alcohol to extract the bioactive compounds from the ginseng root. However, if you’re looking for alternative extraction methods, here are a few you could consider:
Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE): This method involves using a supercritical fluid, often carbon dioxide, as the solvent to extract the desired compounds from ginseng. Supercritical fluids have properties of both liquids and gases, which can enhance their solvating power. This method can result in a highly concentrated extract without the use of harsh solvents.
Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE): Microwaves can be used to heat the extraction solvent and ginseng mixture, which can accelerate the extraction process. This method is known for its efficiency and reduced extraction time compared to traditional methods.

Ultrasound-Assisted Extraction (UAE): Ultrasound waves create cavitation in the extraction solvent, generating localized pressure changes that help break down cell walls and enhance the extraction process. This method can improve extraction efficiency and reduce the required extraction time.
Enzyme-Assisted Extraction: Enzymes can be used to break down the cell walls of the Ginseng Extract, facilitating the release of bioactive compounds. This method is often combined with other extraction methods, such as water or alcohol extraction, to enhance their efficiency.
Pressurized Liquid Extraction (PLE): Also known as accelerated solvent extraction, PLE involves applying both heat and pressure to the extraction solvent, which enhances the solubility of the target compounds and increases extraction efficiency.
Pulsed Electric Fields (PEF) Extraction: PEF involves applying short, high-voltage electrical pulses to the ginseng root, which creates pores in cell membranes, facilitating the release of intracellular compounds.
Subcritical Water Extraction: This method involves using water at temperatures below its boiling point under high pressure. Subcritical water can have enhanced solubility for certain compounds, making it an interesting alternative solvent.
Hydrodistillation: This is a traditional method used for extracting essential oils from plant material. It involves using water and heat to vaporize and then condense the essential oils.
Before using any alternative extraction method, it’s important to consider factors such as the specific bioactive compounds you’re targeting, the safety of the chosen solvent or method, equipment availability, and the potential impact on the final product’s quality. Each method has its own advantages and limitations, so thorough research and experimentation are crucial to determine the most suitable alternative extraction method for your needs.
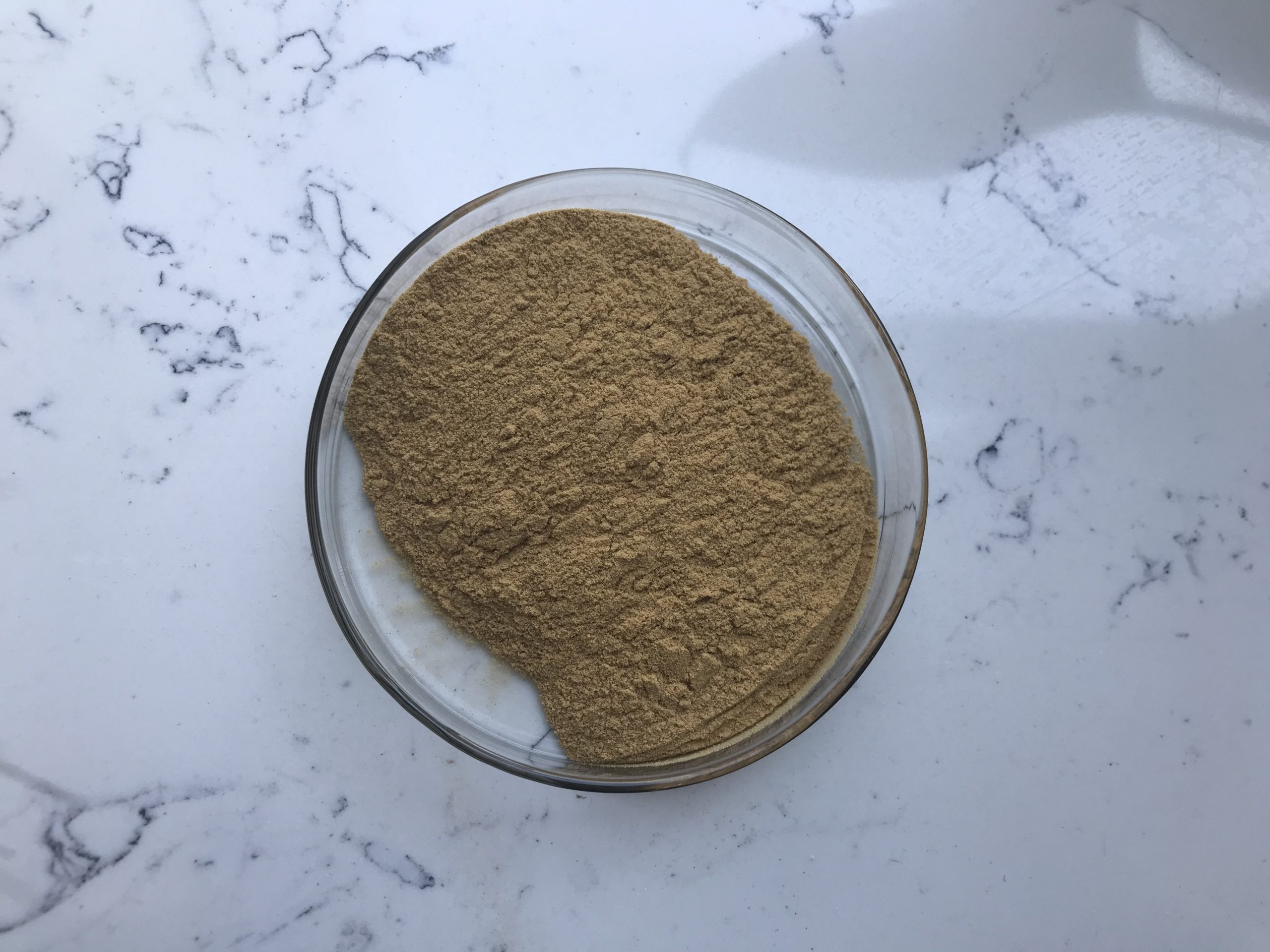
The basic ingredients of Ginseng Extract
Ginseng Extract is derived from the root of the ginseng plant (Panax ginseng). This plant has been used for centuries in traditional medicine, particularly in Asian cultures, due to its potential health benefits. Ginseng root can be processed into various forms, including powder. The basic ingredient of ginseng powder is, of course, ginseng root. Here’s some information about the root and the process of making ginseng powder:
1. Ginseng Root: The primary ingredient of ginseng powder is the ginseng root itself. The root is carefully harvested from mature ginseng plants, usually after several years of growth. The age of the plant can affect the concentration of active compounds in the root.
2. Processing: Once the ginseng root is harvested, it undergoes a series of processes to transform it into powder form. These processes typically include cleaning, drying, and grinding:
- Cleaning: The harvested roots are cleaned to remove dirt and debris.
- Drying: The cleaned roots are dried using methods such as air drying or low-heat drying to remove moisture. This helps to preserve the active compounds in the root.
- Grinding: The dried ginseng roots are ground into a fine powder using specialized equipment. This powder is what we refer to as ginseng powder.
3. Active Compounds: Ginseng Extract contains various bioactive compounds that are believed to contribute to its potential health benefits. These compounds include ginsenosides, which are considered the primary active components responsible for the adaptogenic and immune-supporting effects of ginseng.
4. Potential Benefits: Ginseng is believed to have a range of potential health benefits, which may include boosting energy, supporting the immune system, improving cognitive function, and reducing stress. However, it’s important to note that the effectiveness of ginseng for these purposes is still a topic of ongoing research, and individual responses can vary.
When using Ginseng Extract, it’s important to follow the recommended dosage guidelines and consult with a healthcare professional, especially if you have any underlying health conditions or are taking medications. Additionally, keep in mind that ginseng is not suitable for everyone, and some individuals may experience side effects or interactions with other medications.
Please note that the information provided here is based on the knowledge available up until September 2021. There may have been developments or changes since that time.
