Curcumin is a naturally occurring compound primarily sourced from the Curcuma longa plant, commonly known as turmeric. Turmeric, a yellow-colored spice used extensively in South Asian cuisine, contains 2-8% curcuminoids, with curcumin being the most active and researched of these compounds. The rhizomes (underground stems) of the turmeric plant are harvested, dried, and powdered to extract curcumin, which is used for its potential health benefits, including anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
Curcumin can also be found in dietary supplements, where it is often combined with black pepper extract (piperine) to improve its bioavailability.

Origin, properties and introduction of Curcumin
Origin of Curcumin
Curcumin is a natural compound found in the root of Curcuma longa, commonly known as turmeric, a plant that belongs to the ginger family (Zingiberaceae). Turmeric is widely cultivated in Southeast Asia, especially in India, where it has been used for centuries in traditional medicine (Ayurveda) and as a culinary spice. Curcumin is the primary bioactive compound in turmeric, responsible for its bright yellow color and many of its health-promoting properties.
Properties of Curcumin
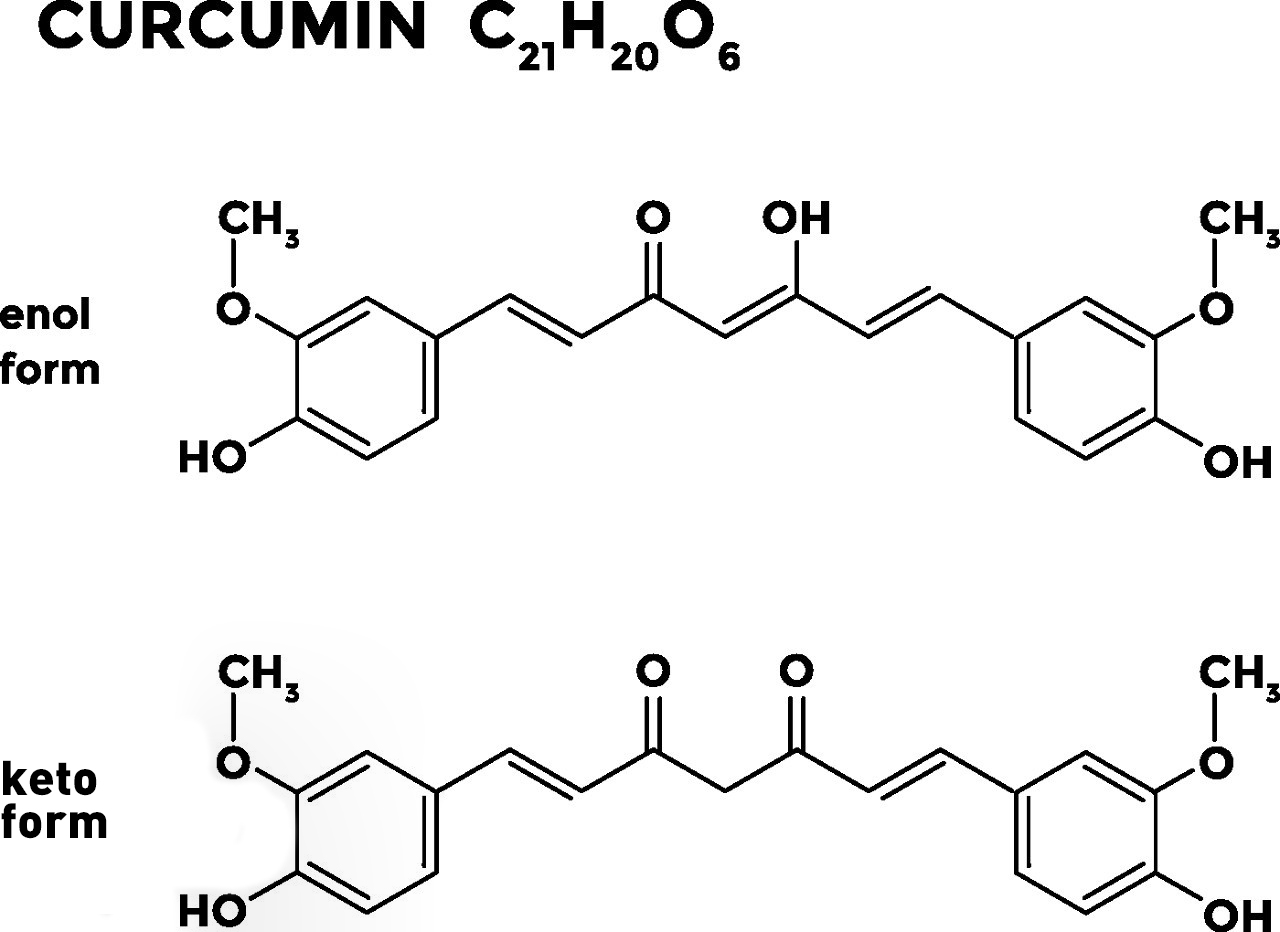
- Chemical Structure: Curcumin is a polyphenol with the chemical formula C₀H₀₄. It is a diarylheptanoid, meaning it contains two aromatic rings connected by a seven-carbon chain. This structure is believed to contribute to curcumin’s antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
- Antioxidant: Curcumin scavenges free radicals, reduces oxidative stress, and increases the activity of the body’s antioxidant enzymes.
- Anti-inflammatory: Curcumin inhibits multiple pathways associated with inflammation by targeting molecules like cytokines and enzymes, such as cyclooxygenase and lipoxygenase.
- Antimicrobial: Curcumin has been shown to have antibacterial, antiviral, and antifungal properties, making it useful in preventing or managing infections.
- Anti-cancer: Curcumin has been found to suppress tumor growth and proliferation by targeting various molecular pathways involved in cancer development.
- Neuroprotective: Curcumin can cross the blood-brain barrier, making it potentially useful for brain health. It may help in conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease by reducing inflammation and oxidative damage.
- Poor Bioavailability: Despite its many health benefits, curcumin has low bioavailability, meaning it is poorly absorbed, metabolized quickly, and eliminated from the body. Various strategies, such as combining curcumin with piperine (found in black pepper) or using lipid-based formulations, can improve its bioavailability.
Introduction to Curcumin
Curcumin has been extensively studied for its therapeutic potential and has gained attention as a dietary supplement and natural remedy for various health conditions. Although curcumin itself has limitations in terms of absorption and bioavailability, it is commonly used in a range of products such as powders, capsules, and creams, and it remains a popular focus of research for its potential to prevent or manage diseases such as cancer, heart disease, arthritis, and neurological disorders.
