Isolating and identifying Bacillus pumilus involves several steps, typically starting from environmental samples. Here’s a general outline of the process:
1.Sample Collection
- Collect samples from environments where Bacillus pumilus is likely to be present, such as soil, water, or plant material.
2. Enrichment Culture
- Inoculate a suitable growth medium (e.g., nutrient broth or selective media) to enrich for Bacillus species. Incubate at 30-37°C for 24-48 hours.
3. Isolation
- After enrichment, streak the culture onto agar plates (e.g., Nutrient Agar or Bacillus-specific media) to isolate single colonies. Incubate under appropriate conditions (aerobic, at 30-37°C).
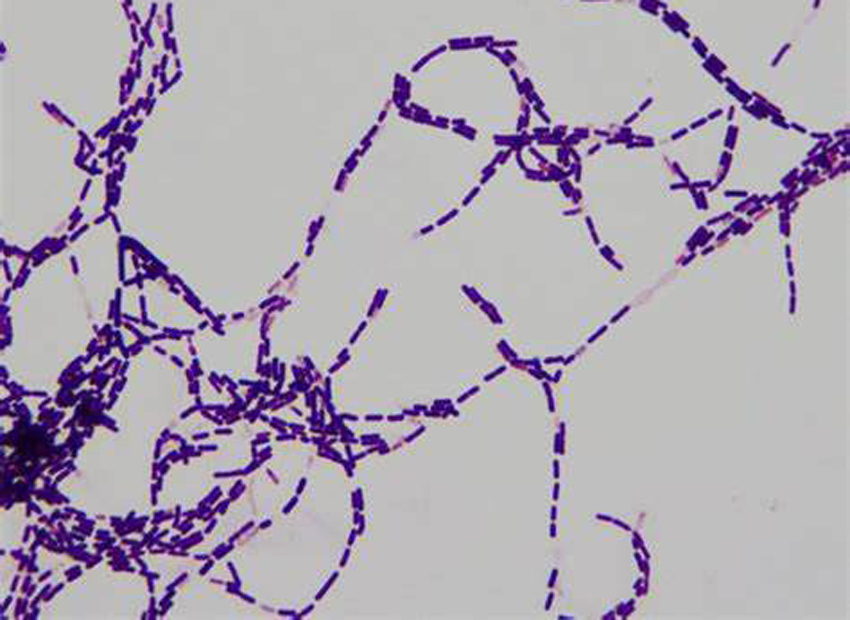
4. Morphological Observation
- Examine colonies for characteristics typical of Bacillus pumilus: rough, irregular edges, and a white to cream color. Use microscopy to observe cell shape (rod-shaped) and gram staining (gram-positive).
5. Biochemical Testing
Perform biochemical tests to confirm identity. Common tests include:
- Catalase test (positive for B. pumilus)
- Indole production (typically negative)
- Lactose fermentation (typically negative)
- Other specific tests like citrate utilization and starch hydrolysis.
6. Molecular Identification
- DNA Extraction: Extract genomic DNA from the isolated strain.
- PCR Amplification: Use specific primers for Bacillus pumilus (often targeting the 16S rRNA gene).
- Gel Electrophoresis: Run the PCR products to check for amplification.
- Sequencing: Sequence the PCR products and compare them to known sequences in databases (like NCBI) to confirm identity.

7. Phylogenetic Analysis (if needed)
- Perform a phylogenetic analysis using the obtained sequences to place Bacillus pumilus within the broader context of related species.
Safety and Handling
- Follow appropriate biosafety protocols when working with bacterial cultures.
This workflow will help you isolate and identify Bacillus pumilus from environmental samples. Let me know if you need more details on any specific step!
