Nattokinase is an enzyme that is derived from natto, a traditional Japanese food made from fermented soybeans. The enzyme is known for its fibrinolytic (clot-dissolving) activity and has been studied for its potential cardiovascular benefits. Here is a general overview of the material and method for obtaining nattokinase:
Material of Nattokinase:
1.Soybeans: Nattokinase is primarily derived from soybeans, which undergo a fermentation process to produce natto. Non-genetically modified (non-GMO) soybeans are often preferred.
2.Bacillus subtilis: The fermentation of soybeans to produce natto involves the use of the bacterium Bacillus subtilis. This bacterium produces nattokinase during the fermentation process.
3.Fermentation Culture Medium: A suitable culture medium is used to support the growth of Bacillus subtilis during the fermentation process. This medium typically includes nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, and minerals.
4.Fermentation Vessels: Containers or vessels where the fermentation of soybeans by Bacillus subtilis takes place. These vessels need to be designed to maintain optimal conditions for bacterial growth.
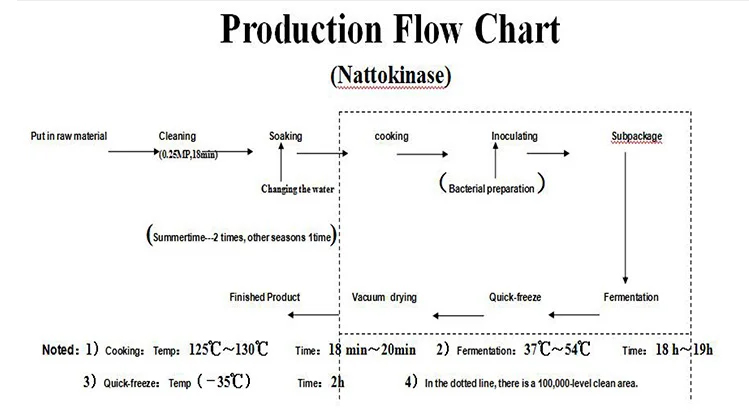
Method of Nattokinase:
1.Soybean Preparation:
Clean and wash soybeans.
Steam the soybeans to make them more suitable for fermentation.
2.Inoculation:
Introduce Bacillus subtilis to the soybeans. This can be achieved by adding a small amount of natto from a previous batch or using a starter culture containing Bacillus subtilis.
3.Fermentation:
Maintain optimal fermentation conditions, including temperature and humidity, to allow Bacillus subtilis to grow and produce nattokinase.
The fermentation process typically takes around 24-48 hours.
4.Harvesting:
After fermentation, the resulting product is natto, which contains nattokinase.
Harvest the natto and separate the liquid portion containing nattokinase from the solid soybeans.
5.Processing:
Extract nattokinase from the liquid portion through processes such as filtration and purification.
The extracted nattokinase may undergo further processing steps to concentrate and purify the enzyme.

6.Drying (Optional):
In some cases, the nattokinase extract may be dried to form a powder for easier storage and transportation.
7.Quality Control:
Conduct quality control tests to ensure the potency, purity, and safety of the nattokinase product.
It’s important to note that specific details of the process may vary among manufacturers, and the production of nattokinase may be subject to regulatory standards to ensure product quality and safety. Additionally, scientific research continues to explore the potential health benefits and applications of nattokinase.
