Nicotinamide, also known as niacinamide or vitamin B3, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in various biochemical processes in the body. It is often used in laboratory settings for research purposes and in the pharmaceutical and cosmetic industries. Below are the materials and methods typically associated with the handling, preparation, and analysis of nicotinamide in a laboratory context:
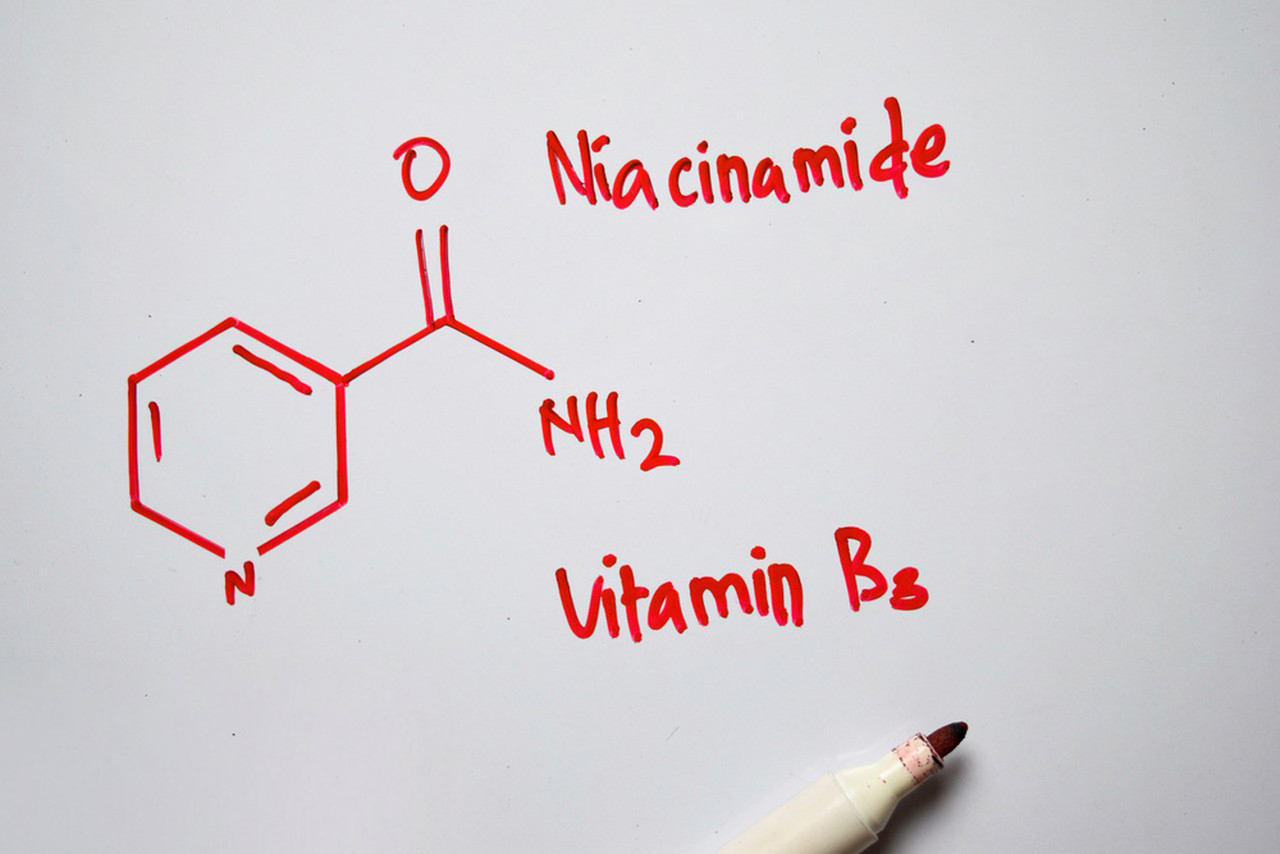
Materials of Nicotinamide:
- Nicotinamide (Niacinamide): The pure compound is required for experiments. It can be purchased from chemical suppliers.
- Solvents: Common solvents like water, ethanol, methanol, or acetonitrile may be required for various experiments involving nicotinamide.
- Laboratory Glassware: This includes beakers, flasks, pipettes, and test tubes for preparing solutions and conducting experiments.
- Chemical Reagents: Depending on the specific experiment, various chemical reagents may be needed for reactions or analyses.
- Analytical Instruments: Equipment such as spectrophotometers, high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography (GC), and mass spectrometers may be used for analysis and quantification of nicotinamide.
- pH Meter: Nicotinamide solutions may require pH adjustment, so a pH meter is essential for accurate measurements.
Methods of Nicotinamide:
- Sample Preparation: Nicotinamide can be dissolved in an appropriate solvent to create stock solutions of known concentrations. These solutions can be further diluted as needed for specific experiments.
- HPLC/GC Analysis: High-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) or gas chromatography (GC) can be used to separate and quantify nicotinamide in a sample. A suitable detector, such as a UV-Vis detector for HPLC, is used to detect the compound.
- Spectrophotometry: Nicotinamide can be analyzed using UV-Vis spectrophotometry. A UV-Vis spectrophotometer is used to measure the absorbance of nicotinamide solutions at specific wavelengths, which can then be correlated with concentration.
- pH Adjustment: If the pH of the solution needs to be adjusted, acid or base solutions can be added while monitoring the pH using a pH meter.
- HPLC/GC Method Development: The development of an HPLC or GC method for nicotinamide analysis involves selecting appropriate columns, mobile phases, and detection conditions to achieve accurate and reproducible results.
- Sample Analysis: Nicotinamide-containing samples are injected into the HPLC or GC instrument, and the chromatograms or spectra are recorded. Concentrations can be calculated based on standard curves or calibration curves.
- Data Analysis: Data obtained from the analysis are processed using appropriate software to calculate concentrations, peak areas, and other relevant parameters.
- Quality Control: Quality control measures are implemented to ensure the accuracy and precision of the analysis, including running standard reference materials and replicates.
- Safety Precautions: Standard laboratory safety practices, including the use of personal protective equipment (PPE) and proper handling and disposal of chemicals, should be followed at all times.
It’s important to note that the specific methods and materials used for nicotinamide analysis can vary depending on the nature of the experiment and the equipment available in the laboratory. Researchers should refer to established protocols and safety guidelines when working with nicotinamide or any other chemical compound.
