Royal Jelly Powder is a nutritious substance produced by worker bees to feed the queen bee and young bees in a colony. It is a complex mixture of proteins, sugars, vitamins, and minerals, and it has been used in traditional medicine for its potential health benefits. Here are the materials and methods typically involved in the production and harvesting of royal jelly:
Materials of Royal Jelly Powder:
Beehives: Royal jelly is collected from beehives, so you need a beehive populated with honey bees. The hive should be well-maintained and have a strong, healthy colony.
Queen bee: The royal jelly is produced to feed the queen bee, so a queen bee is required in the hive.
Queen excluder: To ensure that the queen bee does not lay eggs in the cells containing royal jelly, a queen excluder is placed between the brood chamber and the super chamber.
Larvae: Worker bees select young larvae to feed royal jelly. These larvae are typically 1-3 days old.
Royal jelly cups: Small cups or cells are placed on frames within the hive for the worker bees to deposit royal jelly.
Harvesting tools: Specialized tools are used for harvesting royal jelly, including a royal jelly knife or spatula.

Methods of Royal Jelly Powder:
Identifying the right time: Royal Jelly Powder is produced by worker bees when they need to feed the queen bee and newly hatched larvae. To harvest royal jelly, you need to identify the right time when it’s abundant in the hive. This typically occurs during the first 3 days of a larva’s life.
Preparation of the hive: The hive should be well-maintained and have a strong, healthy colony. A queen excluder should be placed to prevent the queen from entering the super chamber where the royal jelly is deposited.
Selecting larvae: Worker bees select young, 1-3 day old larvae that are suitable for producing royal jelly. These larvae are placed in specially prepared royal jelly cups.
Feeding the larvae: Worker bees feed the selected larvae a diet of royal jelly, which they produce by secreting it from their hypopharyngeal glands. The royal jelly is deposited into the royal jelly cups.
Harvesting: After 3 days, the royal jelly is harvested. A specialized tool, like a royal jelly knife or spatula, is used to carefully collect the royal jelly from the cups.
Storage: Royal jelly is highly perishable and must be stored at low temperatures to maintain its freshness and nutritional properties. It is often frozen or freeze-dried for long-term storage.
Processing: Royal jelly can be processed into various forms, including fresh royal jelly, freeze-dried royal jelly, or royal jelly capsules, for commercial use.
It’s important to note that harvesting royal jelly should be done carefully to minimize disturbance to the hive and ensure the well-being of the bees. Proper beekeeping knowledge and practices are essential to ensure sustainable and ethical royal jelly production.
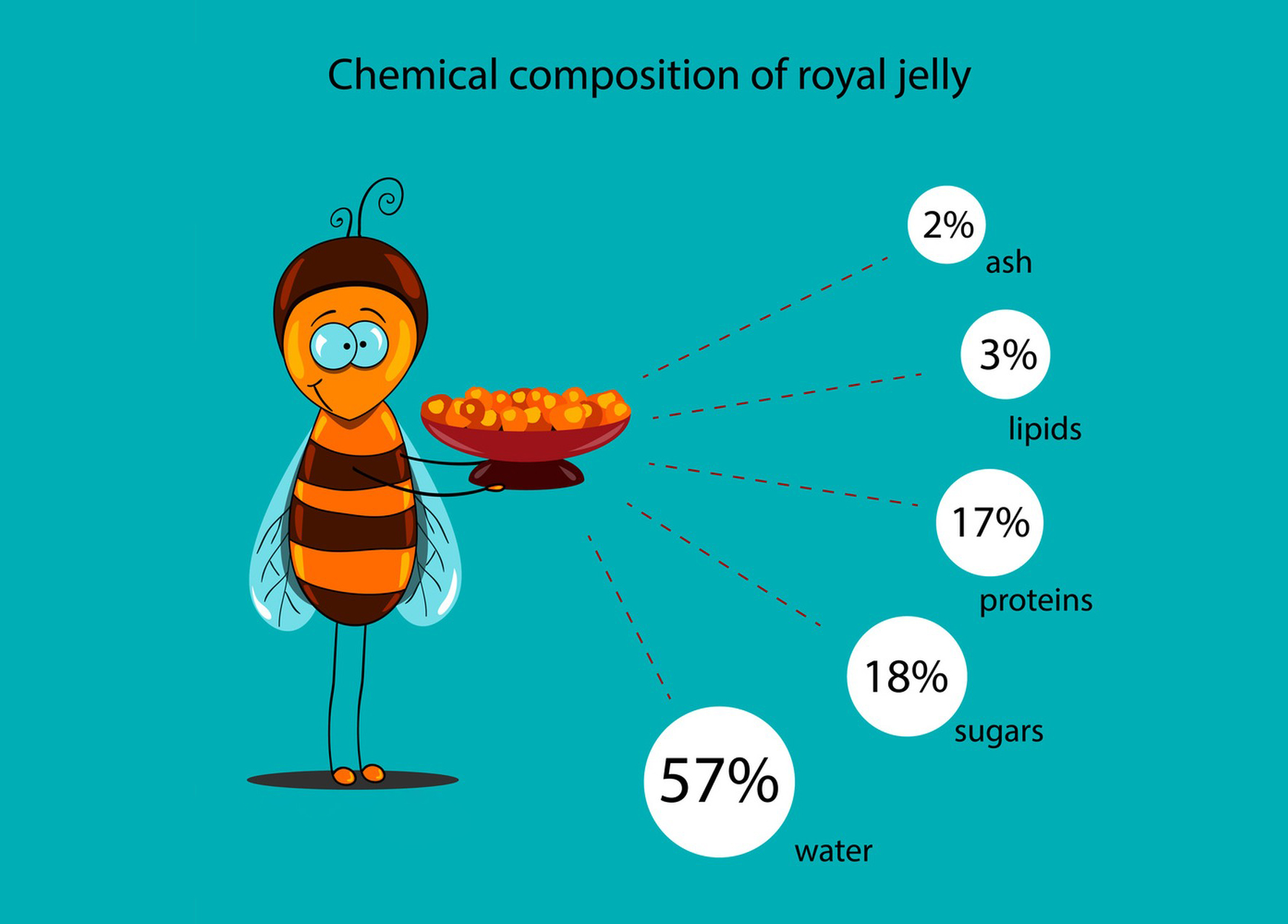
The process of Royal Jelly Powder
Royal Jelly Powder is a thick, milky substance secreted by worker bees to feed and nourish the queen bee and the young larvae in a honeybee colony. It plays a crucial role in the development and differentiation of bee larvae. Here’s a general overview of the process of royal jelly production:
1.Worker Bee Secretion:
Royal jelly is produced by the hypopharyngeal glands of young worker bees (nurse bees). These glands are highly developed in worker bees between 5 and 15 days old, which is when they are responsible for feeding the queen bee and young larvae.
2.Collection:
Worker bees transfer royal jelly into their mouths and then transfer it into the mouths of the queen bee and the young larvae. The nurse bees collect the royal jelly and store it in their crop (an expandable storage organ) temporarily before regurgitating it into the cells containing the developing larvae.
3.Feeding Queen Bee:
The queen bee is continuously fed royal jelly throughout her entire life, which can be several years. This specialized diet of royal jelly triggers the development of her reproductive organs and extends her lifespan significantly. The royal jelly ensures that she can lay eggs efficiently.
4.Feeding Larvae:
Royal Jelly Powder is also fed to the young bee larvae during the first three days of their development. This special diet causes some larvae to develop into queens, while others become worker bees. The amount and duration of royal jelly feeding determine the caste (queen or worker) a larva will become. Queen larvae are fed royal jelly exclusively, which leads to their larger size and reproductive capability.
5.Harvesting Royal Jelly:
Beekeepers can harvest royal jelly by introducing artificial queen cells into a hive. The nurse bees will fill these cells with royal jelly, which can then be collected. To harvest, beekeepers typically use a small spatula or vacuum pump to carefully remove the royal jelly from the cells.
6.Processing:
After harvesting, the royal jelly is typically processed and preserved. This may involve freezing, drying, or mixing it with other substances to create various royal jelly products, such as capsules, creams, or dietary supplements for human consumption.
It’s important to note that royal jelly is highly perishable, so it needs to be handled and stored carefully to maintain its quality and freshness.
Royal Jelly Powder has gained attention for its potential health benefits in humans, but more research is needed to confirm these claims, and individuals with allergies or other health concerns should exercise caution when using royal jelly products.
