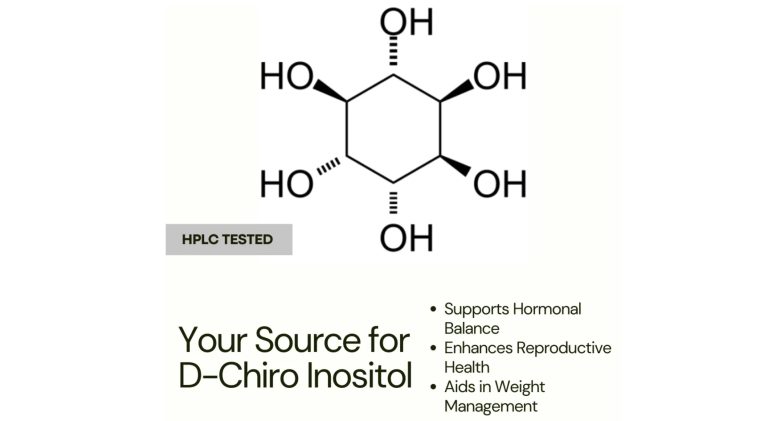
Chemical Structure and Physical Properties of D-Chiro-Inositol
D-Chiro-Inositol (DCI) is a stereoisomer of inositol, which is a cyclohexanehexol (six-carbon cyclic polyol with six hydroxyl groups). Chemical Structure 1. Chemical formula: C₆H₁₂O₆ 2. Molecular weight: 180.16 g/mol 3. IUPAC name: (1R,2S,3R,4S,5S,6S)-Cyclohexane-1,2,3,4,5,6-hexol 4. Stereochemistry: It has six chiral centers; the “D-Chiro”…