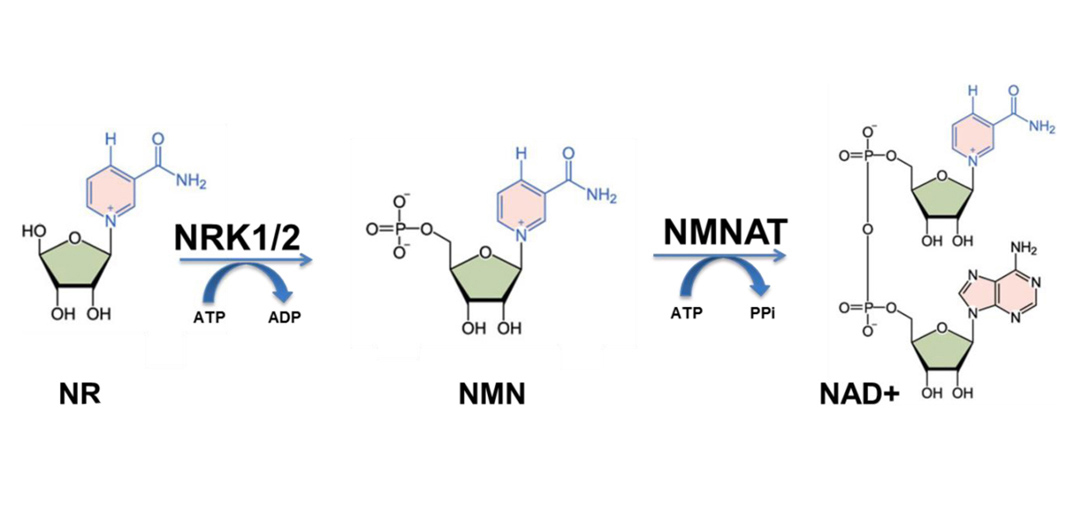
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is a form of vitamin B3 that is used to boost levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) in the body. NAD+ plays a key role in energy metabolism, DNA repair, and other cellular processes. While Nicotinamide riboside is generally considered safe, it can interact with certain substances, and it’s important to be mindful of how it may combine with other supplements, medications, or dietary factors.
Here are some potential interactions:
1. Medications:
- Chemotherapy drugs: There is some research suggesting that increasing NAD+ levels with supplements like Nicotinamide riboside could affect the response to chemotherapy treatments, as NAD+ is involved in DNA repair mechanisms. It may enhance the survival of cancer cells, although this needs more study. It’s essential to consult with a doctor before taking NR if you’re undergoing cancer treatment.
- Blood pressure medications: Nicotinamide riboside might influence cardiovascular health and may interact with medications used for blood pressure regulation. Some studies suggest that Nicotinamide riboside can improve vascular function, which could alter how these medications work in the body.
- Diabetes medications: As Nicotinamide riboside has effects on metabolism and cellular energy, it might interact with drugs used for controlling blood sugar levels. While it’s thought to be beneficial for metabolic health, its impact alongside insulin or other diabetes medications should be monitored.

2. Supplements:
- Other NAD+ precursors (e.g., NMN): Both nicotinamide riboside (NR) and nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) are used to boost NAD+ levels. Combining them could potentially have a synergistic effect, but the long-term effects of taking them together are not well-established. Most people choose one or the other, but some research suggests that combining them could provide additional benefits.
- Antioxidants: Some studies indicate that Nicotinamide riboside may work in synergy with antioxidants, like resveratrol or curcumin, which also support NAD+ levels or cellular health. However, combining large doses of multiple antioxidants could potentially lead to imbalances in oxidative stress levels.
- Vitamin B3 forms (niacin, nicotinamide): Taking large doses of other forms of vitamin B3 alongside Nicotinamide riboside might result in excess NAD+ synthesis. However, these forms of B3 typically have different effects, so the combination may be less of a concern.
3. Dietary Factors:
- Alcohol: Alcohol consumption can impact NAD+ levels because it depletes NAD+ in the liver as it metabolizes alcohol. Nicotinamide riboside supplementation could help offset this depletion, though it doesn’t eliminate the harmful effects of alcohol on the liver and other organs.
- High-fat diet: Some animal studies have shown that a high-fat diet may reduce the effectiveness of Nicotinamide riboside supplementation, possibly because of altered metabolic pathways. However, more human studies are needed to confirm this effect.
4. Other Potential Interactions:
- Sirtuin-activating compounds (e.g., resveratrol): Sirtuins are proteins that help regulate cellular health and longevity, and they require NAD+ to function. Combining Nicotinamide riboside with sirtuin-activating compounds might have a synergistic effect on cellular health, but this needs more research to understand the optimal dosing and long-term effects.
As always, it’s a good idea to talk to a healthcare professional before starting Nicotinamide riboside supplementation, especially if you’re taking other medications or supplements, to ensure there are no interactions that could affect your health.
