Epitalon, also known as epithalamin, is a synthetic peptide derived from the pineal gland peptide called epithalamine. The pineal gland is a small endocrine gland located in the brain that produces melatonin, a hormone involved in regulating sleep-wake cycles. Epitalon was first discovered and studied in the 1980s by Russian scientist Professor Vladimir Khavinson and his team.
Here are some key aspects of Epitalon:
1.Origin:
Epitalon is based on the natural peptide called epithalamine, which is extracted from the pineal gland of animals. However, the synthetic version of this peptide, known as Epitalon, is created through laboratory processes. The peptide sequence of Epitalon is alanine-glutamate-asparagine-glycine.
2.Nature:
Epitalon is a tetrapeptide, meaning it consists of four amino acid residues. Amino acids are the building blocks of proteins, and peptides are short chains of amino acids. Epitalon is specifically designed to mimic the structure of the natural pineal gland peptide and is believed to have anti-aging properties.
3.Introduction:
The introduction of Epitalon is primarily associated with the research conducted by Professor Vladimir Khavinson. He and his team focused on the role of peptides in the regulation of various physiological processes, including aging. Their studies suggested that Epitalon might have potential anti-aging effects by influencing the activity of the pineal gland and related biological pathways.

4.Anti-Aging Properties:
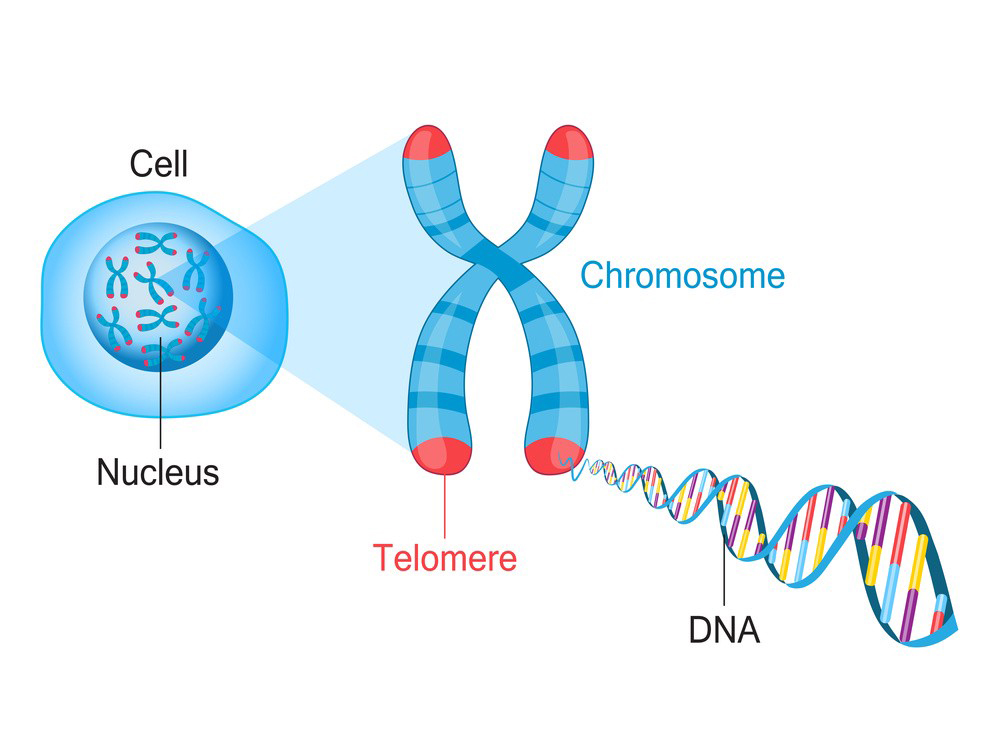
Epitalon is often touted for its purported anti-aging properties. Some studies suggest that it may help regulate the production of melatonin and other hormones, potentially influencing the aging process. It is believed to work by stimulating the production of telomerase, an enzyme that plays a role in maintaining the length of telomeres, which are protective caps on the ends of chromosomes. Shortened telomeres are associated with aging and age-related diseases.
5.Research and Controversies:
While there is some research suggesting potential benefits of Epitalon, it’s essential to note that the scientific community is still exploring its effects, and more rigorous studies are needed to establish its safety and efficacy definitively. Additionally, there may be controversies and debates surrounding the use of peptides for anti-aging purposes.
It’s crucial to approach claims about the anti-aging properties of Epitalon with caution and consult with healthcare professionals before considering its use, as the field of anti-aging interventions is complex and continuously evolving.
Potential Benefits of Epitalon
Epitalon, also known as epithalamin, is a synthetic peptide derived from the pineal gland peptide called epithalamine. It has been studied for its potential anti-aging and health-promoting effects. However, it’s important to note that research on Epitalon is still in the early stages, and more rigorous clinical studies are needed to establish its efficacy and safety conclusively. As of my last knowledge update in January 2022, here are some potential benefits associated with Epitalon:
1.Telomere Extension:
Epitalon is believed to stimulate the production of telomerase, an enzyme that helps protect and extend the length of telomeres. Telomeres are the protective caps at the ends of chromosomes, and their length is associated with cellular aging. Maintaining telomere length may be linked to improved cell function and longevity.
2.Anti-Aging Effects:
Some studies suggest that Epitalon may have anti-aging effects by influencing key biological processes, such as telomere length, oxidative stress, and inflammation. These factors play a role in the aging process, and addressing them could potentially slow down aging-related changes.
3.Immune System Support:
Epitalon has been investigated for its potential to enhance immune function. By modulating the activity of immune cells, it may help improve the body’s ability to defend against infections and diseases.
4.Neuroprotective Properties:
There is some evidence to suggest that Epitalon may have neuroprotective effects. It may help protect neurons from damage and support overall brain health. This could potentially have implications for cognitive function and age-related neurodegenerative conditions.
5.Regulation of Circadian Rhythms:
The pineal gland, where Epitalon is derived from, plays a role in the regulation of circadian rhythms and the production of melatonin. Epitalon may influence these processes, potentially contributing to better sleep and overall circadian rhythm regulation.
It’s crucial to approach claims about the benefits of Epitalon with caution, as more research is needed to confirm and fully understand its effects. Additionally, the regulatory status of Epitalon may vary in different regions, and it may not be approved for medical use in some places. Before considering any peptide or supplement for health-related purposes, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure it is safe and appropriate for individual circumstances.
