Origin and Nature of Phycocyanin:
Phycocyanin is a blue pigment protein primarily found in certain species of cyanobacteria (blue-green algae) and red algae. It belongs to the class of phycobiliproteins, which are light-harvesting pigments that absorb light energy and assist in photosynthesis. Phycocyanin absorbs light in the orange and red regions of the spectrum (600–650 nm) and reflects blue light, giving it its characteristic blue color.
Phycocyanin is composed of two main subunits: α and β chains, which form a heterodimer. It contains a chromophore called phycocyanobilin, which is responsible for its absorption and emission properties. Phycocyanin is typically water-soluble and can be extracted from cyanobacteria or algae, and is widely used for various applications due to its vibrant color and potential health benefits.
Natural Sources:
- Cyanobacteria (Blue-Green Algae): The primary source of phycocyanin. It is abundant in species like Spirulina (Arthrospira), which is commonly used for commercial extraction.
- Red Algae: Phycocyanin is also found in species like Porphyra.
- Other sources: Phycocyanin has been identified in various freshwater and marine cyanobacteria.

Functions in Nature:
Phycocyanin serves as part of the phycobilisome, a light-harvesting complex in cyanobacteria and algae. It helps capture light energy, which is then transferred to chlorophyll for photosynthesis. Phycocyanin is essential for these organisms to utilize light energy efficiently, especially in environments with low light.
Introduction and Applications:
1. Health and Nutritional Benefits:
Phycocyanin has attracted attention in recent years due to its potential antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. It is considered a natural colorant and is increasingly used in the food and cosmetic industries as a natural alternative to synthetic dyes. Some potential health benefits include:
- Antioxidant properties: Phycocyanin helps scavenge free radicals, which can prevent cellular damage.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: It may reduce inflammation and help in managing conditions like arthritis.
- Liver protection: Some studies suggest that phycocyanin can help detoxify the liver.
- Immune support: It may boost immune function by enhancing the production of certain cytokines.
2. Food and Beverage Industry:
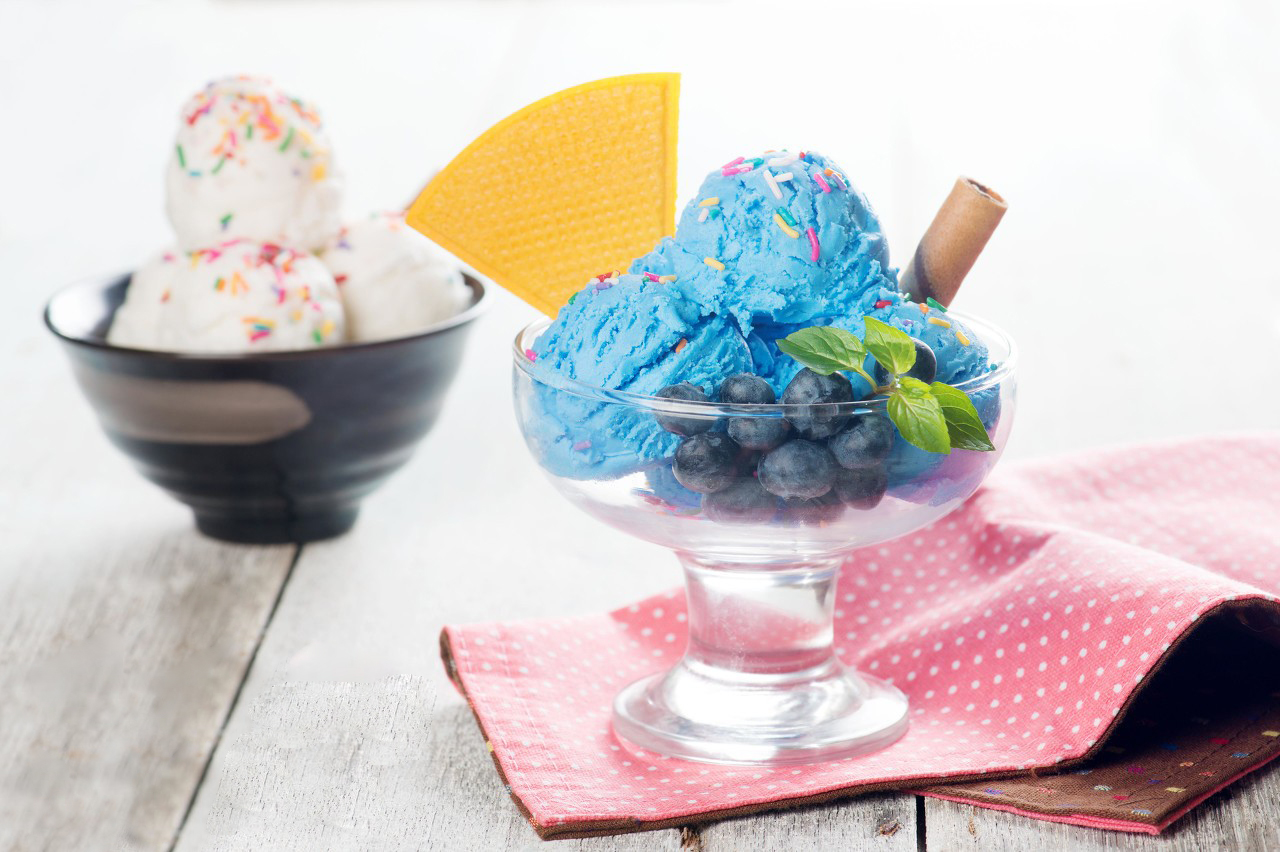
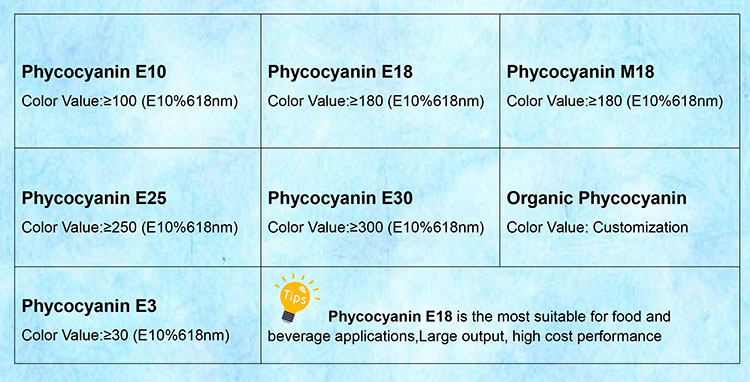
Phycocyanin is widely used as a natural blue food colorant. It is safe and FDA-approved, making it an attractive option for coloring drinks, candies, ice cream, and other food products. Its E-number is E18 (in Europe).
3. Cosmetic Industry:
Due to its vibrant color and potential antioxidant properties, phycocyanin is also used in various skincare and cosmetic products. It can be found in lotions, serums, and masks designed to protect the skin from oxidative stress and environmental damage.
4. Research and Biotechnology:
Phycocyanin has been studied for its potential in biotechnology, such as bioengineering and as a biosensor. Researchers have also explored its use in drug delivery systems and nanotechnology.
5. Sustainable Alternatives:
As a natural pigment, phycocyanin is often seen as a more sustainable and safer alternative to synthetic dyes, which can have adverse environmental impacts and potential health risks.
Extraction of Phycocyanin:
The extraction process usually involves harvesting the cyanobacteria (such as Spirulina), followed by:
- Cell disruption: This can be achieved through various methods such as sonication, freeze-thawing, or mechanical disruption.
- Purification: Phycocyanin is often isolated using techniques like chromatography or filtration.
The resulting phycocyanin can be used in various products, from food additives to pharmaceuticals.
In summary, phycocyanin is a highly versatile and valuable natural product derived from cyanobacteria and red algae. Its applications span across health, food, cosmetics, and research, making it a key player in the ongoing shift towards more sustainable and natural solutions in various industries.
