Arachidonic Acid is a long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid (PUFA) with 20 carbon atoms and four double bonds. It is an essential fatty acid, which means that it cannot be synthesized by the human body and must be obtained through the diet.
Origin of Arachidonic Acid:
Arachidonic Acid is derived from linoleic acid, another essential fatty acid, which is found in various plant oils, nuts, and seeds. The conversion of linoleic acid to Arachidonic Acid occurs through a series of enzymatic reactions in the body. This process involves the desaturation and elongation of the fatty acid chain.
Properties of Arachidonic Acid:
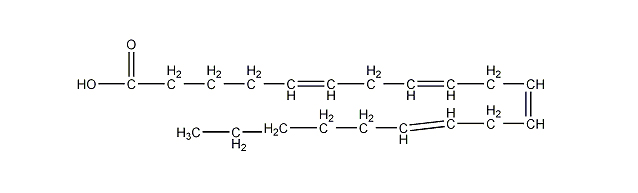
- Structure: Arachidonic Acid has a 20-carbon chain with four double bonds (all-cis configuration). Its chemical formula is C20H32O2.
- Biological role: Arachidonic Acid is a critical component of cell membranes and is involved in various cellular processes. It serves as a precursor for the synthesis of important signaling molecules known as eicosanoids, which include prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes. These eicosanoids play crucial roles in inflammation, blood clotting, and immune response regulation.
Introduction of Arachidonic Acid:
Arachidonic Acid gained significant attention in the 20th century as researchers discovered its importance in human health and disease. It is essential for the proper functioning of the body and is especially important during early development, including fetal development and infancy.
Arachidonic Acid is commonly found in various animal products, such as meat, eggs, and fish. Additionally, it can be obtained from certain plant oils, like evening primrose oil, blackcurrant seed oil, and borage oil, which are rich in its precursor, linoleic acid.
Due to its involvement in inflammation and various disease processes, Arachidonic Acid’s levels and metabolism have been studied in the context of conditions like cardiovascular diseases, rheumatoid arthritis, and cancer. However, it is important to note that the role of Arachidonic Acid in health and disease is complex, and its effects can be influenced by other dietary and lifestyle factors.
As with any nutrient, it is crucial to maintain a balanced intake of Arachidonic Acid as excessive consumption may have adverse effects. People with specific health conditions should always consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians to determine their dietary needs regarding essential fatty acids like Arachidonic Acid.

Efficacy evaluation of Arachidonic Acid
As of my last update in September 2021, Arachidonic Acid (ARA) is an essential omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acid found in various foods, particularly in animal products like meat, eggs, and dairy. It plays a vital role in the human body as a precursor to several important bioactive lipid mediators, such as prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes, which are involved in various physiological processes, including inflammation, immune response, and blood clotting.
The efficacy of Arachidonic Acid has been studied in various contexts, particularly in relation to its role in human health. Here are some areas where its efficacy has been evaluated:
Infant development: Arachidonic Acid is a key component of brain and eye tissue and is crucial for brain development in infants. It is often added to infant formulas to mimic the levels found in breast milk, as breast milk naturally contains Arachidonic Acid and other important nutrients for the baby’s growth and development.
Inflammation and immune response: Arachidonic Acid is a precursor to pro-inflammatory mediators, such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes. The balance of these mediators is essential for proper immune function and inflammation responses in the body. Dysregulation of Arachidonic Acid metabolism has been implicated in various inflammatory conditions.
Sports performance and muscle growth: Some studies have suggested that supplementing with Arachidonic Acid may support muscle growth and enhance exercise performance. However, more research is needed in this area, and the evidence is not yet definitive.

Cardiovascular health: The role of Arachidonic Acid in cardiovascular health is complex. Some studies have shown a potential association between higher levels of Arachidonic Acid in the diet and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease. On the other hand, certain Arachidonic Acid-derived compounds also have cardioprotective effects. More research is needed to fully understand its impact on cardiovascular health.
It’s essential to note that while Arachidonic Acid is essential for certain physiological processes, excessive levels of it or imbalances in its metabolism can lead to health issues. Additionally, individual responses to Arachidonic Acid may vary based on genetic factors, diet, and overall health.
As with any supplement or dietary component, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making any significant changes to your diet or considering Arachidonic Acid supplementation, especially if you have pre-existing health conditions or concerns. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific needs and health status. Also, always rely on the most recent research and consult updated scientific literature, as new findings may have emerged since my last update.
