Origin of Ferulic Acid:
Ferulic acid (4-hydroxy-3-methoxycinnamic acid) is a naturally occurring phenolic compound found in various plant tissues. It was first isolated from ferula (a genus of flowering plants) gum by the French chemist H. Braconnot in 1842. Ferula species, along with other plants like rice bran, oats, and coffee, are notable sources of ferulic acid.

Properties of Ferulic Acid:
Ferulic acid is characterized by its chemical structure, which includes a phenylpropenoic acid structure. It is a type of hydroxycinnamic acid and belongs to the class of phenolic acids. Some of its properties include:
- Antioxidant Activity: Ferulic acid is known for its strong antioxidant properties. It helps neutralize harmful free radicals in the body, which are implicated in various diseases and the aging process.
- UV Protection: It has been used in skincare products due to its ability to absorb and neutralize UV radiation, offering protection against sun damage to the skin.
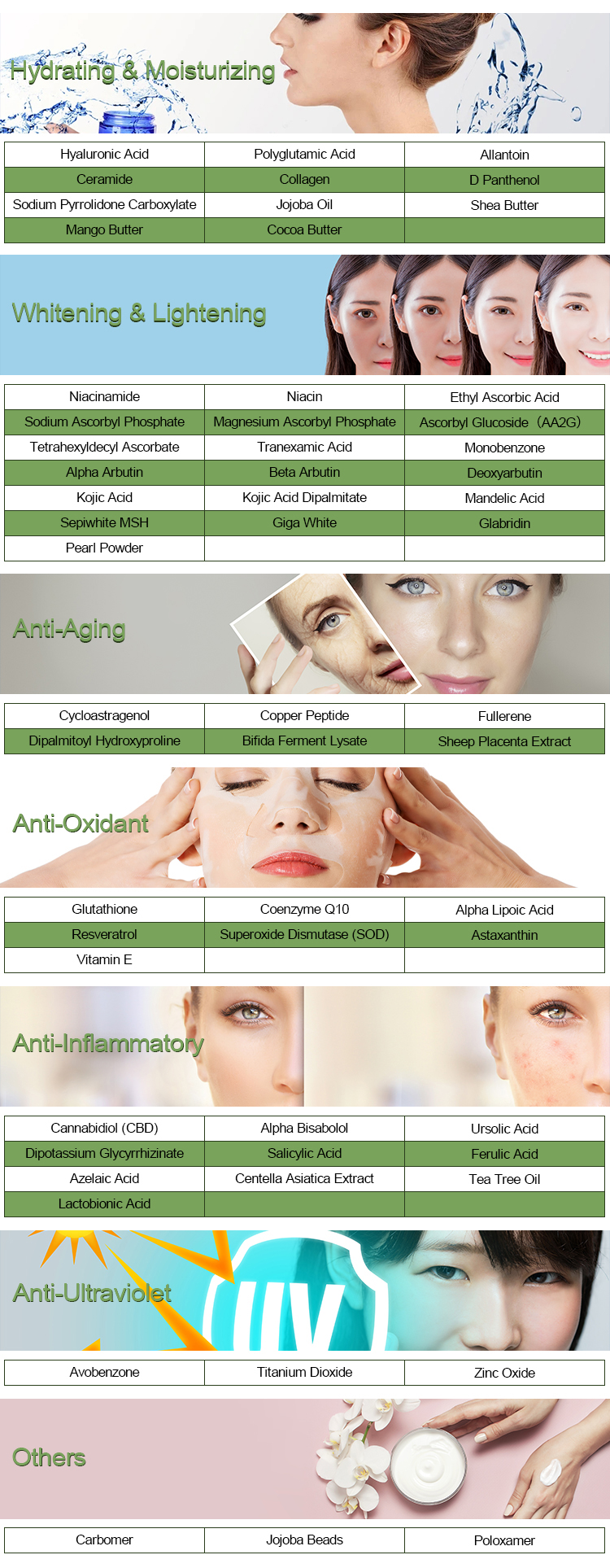
- Anti-Inflammatory: Ferulic acid exhibits anti-inflammatory effects, making it potentially beneficial for reducing inflammation-related conditions.
- Antimicrobial: It has been investigated for its antimicrobial properties against certain bacteria and fungi.
- Plant Cell Wall Component: In plants, ferulic acid is an essential component of the cell walls, contributing to their rigidity and structural integrity.
Introduction and Uses of Ferulic Acid:
Ferulic acid has gained attention in various industries due to its potential health benefits and applications. Some of its notable uses include:
- Cosmetics and Skincare: Ferulic acid is often incorporated into skincare products, such as serums and lotions, to provide antioxidant protection against skin aging caused by environmental stressors like UV radiation and pollution.
- Food Preservation: Ferulic acid is used as a natural antioxidant and preservative in food products to extend shelf life by preventing lipid oxidation.
- Dietary Supplements: It’s available as a dietary supplement due to its potential health benefits, including its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects.
- Pharmaceuticals: Research suggests that ferulic acid may have potential therapeutic applications, including anti-cancer, anti-diabetic, and neuroprotective effects. It might also contribute to cardiovascular health.
- Functional Foods: Ferulic acid-rich foods, like whole grains and fruits, are often promoted for their potential health benefits.
- Plant Biotechnology: Ferulic acid and its derivatives are being explored for their role in plant biotechnology, including enhancing the nutritional content and stress resistance of crops.
It’s important to note that while ferulic acid holds promise in various applications, more research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms of action and potential benefits. As with any bioactive compound, its effects can vary depending on factors such as dosage, formulation, and individual response.
