Gibberellic Acid (GA) is a plant hormone that plays a crucial role in regulating various growth and developmental processes in plants. Here’s some information about its origin, properties, and introduction:
Origin of Gibberellic Acid:
Gibberellic Acid was first discovered in Japan in the 1920s when researchers were investigating a disease affecting rice plants called “foolish seedling disease.” The disease caused excessive stem elongation in the affected plants. The substance responsible for this elongation was later identified as Gibberellic Acid.

Properties of Gibberellic Acid:
Chemical Structure: Gibberellic Acid is a complex organic compound with a tetracyclic diterpenoid structure.
Function: It primarily functions as a growth regulator, promoting stem elongation, germination, and flowering in plants.
Solubility: Gibberellic Acid is soluble in water, which makes it easy to apply as a foliar spray or soil treatment.
Introduction of Gibberellic Acid:
Commercial Production: Gibberellic Acid can be produced synthetically or extracted from certain fungi, particularly species of the fungus Gibberella (formerly known as Fusarium). Commercially, it is often produced through fermentation processes using fungi.
Applications: Gibberellic Acid is widely used in agriculture to control plant growth and development. It is applied to crops to induce flowering, increase fruit size, and promote uniform germination. Additionally, it is used in tissue culture to stimulate the growth of plant cells.
Mode of Action:
Gibberellic Acid affects plant growth by promoting cell elongation and division. It stimulates the production of enzymes that break down starches into simpler sugars, providing the energy needed for cell expansion.
It also influences the expression of genes related to growth processes, including those involved in flowering and seed development.
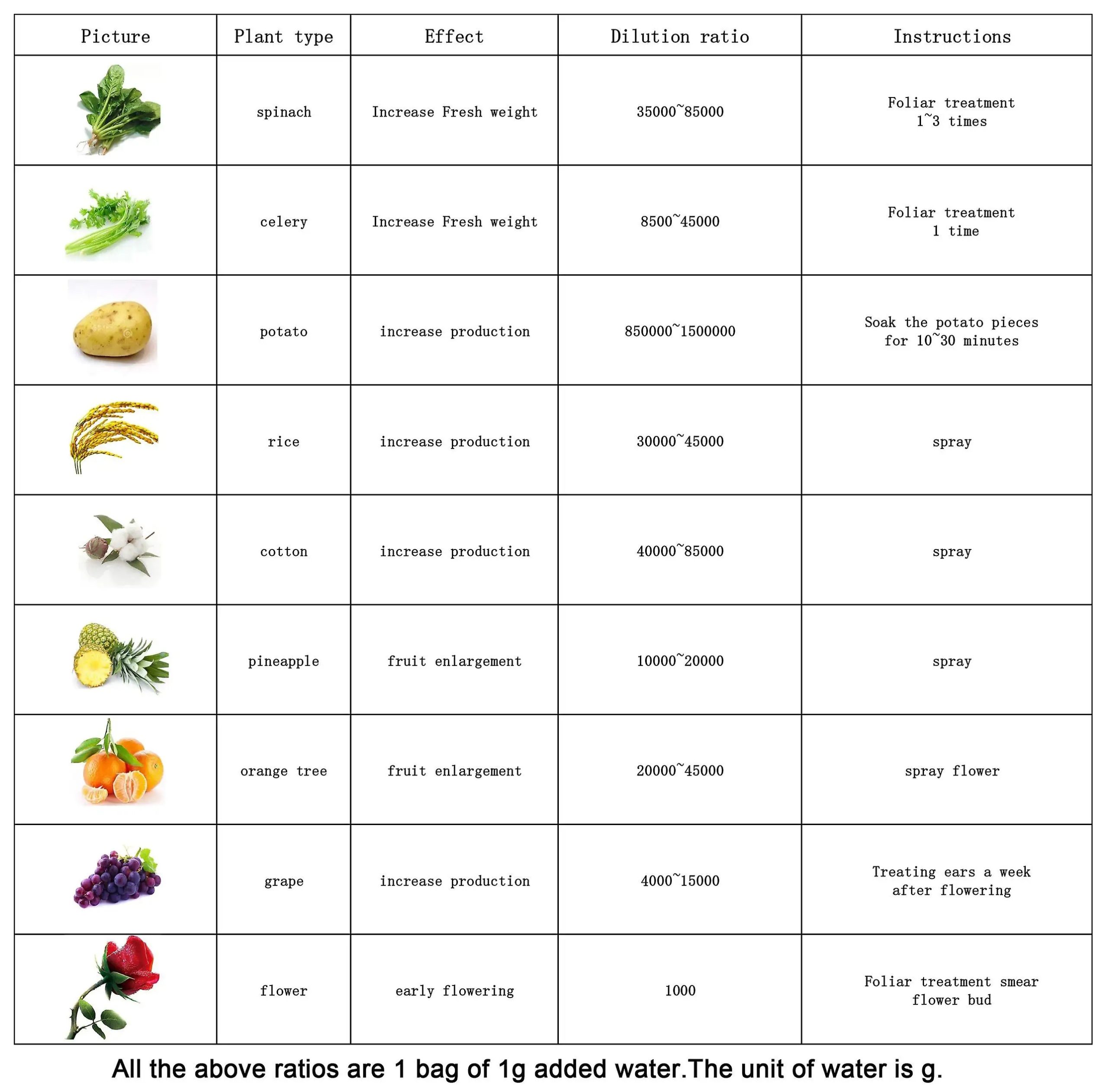
Regulation and Safety:
The use of Gibberellic Acid is regulated in agriculture to ensure safe and effective application.
Safety precautions, dosage recommendations, and application methods are outlined to prevent unintended consequences and to optimize its effects on plant growth.
Gibberellic Acid has proven to be a valuable tool in agriculture, contributing to improved crop yields and the manipulation of plant growth for various purposes. Its applications extend beyond traditional farming to include horticulture, forestry, and research in plant physiology.
