Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA) and Phenylethylamine (PEA) are two different compounds, both with distinct roles and mechanisms of action. Below is a comparison between the two:
1. Chemical Structure
Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA): A fatty acid amide, PEA is a naturally occurring lipid molecule derived from palmitic acid. It is part of the family of endocannabinoids and endovanilloids.
Phenylethylamine (PEA): A biogenic amine and trace amine, PEA is chemically similar to amphetamines. It is a natural monoamine compound derived from the amino acid phenylalanine.
2. Mechanism of Action
Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA):
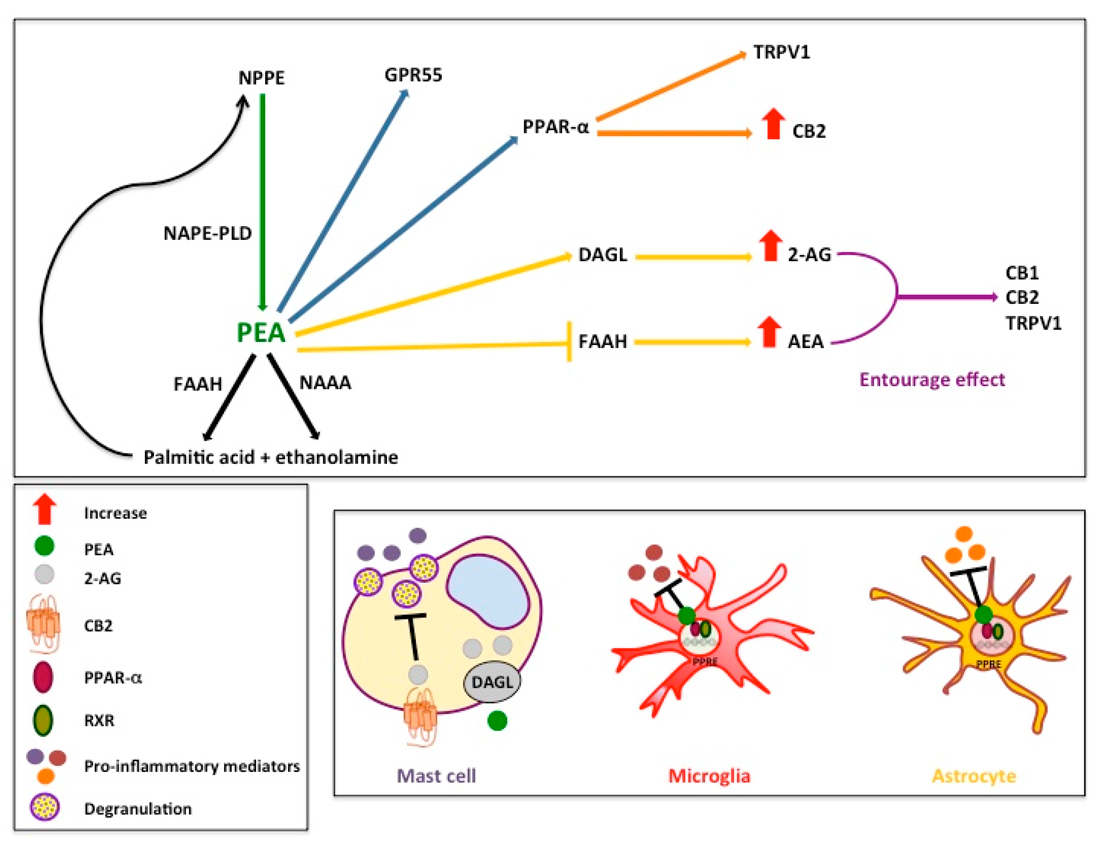
- Palmitoylethanolamide is thought to act primarily by modulating the endocannabinoid system, though it is not a cannabinoid itself. It influences the activity of CB2 receptors and interacts with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs), which are involved in inflammation and cell metabolism.
- It also has anti-inflammatory, analgesic (pain-relieving), and neuroprotective effects, primarily by influencing mast cells and glial cells in the nervous system.
Phenylethylamine (PEA):
- Phenylethylamine is a dopamine and norepinephrine releasing agent, affecting neurotransmitter release in the brain.
- It is often associated with the “feel-good” effects, as it promotes mood elevation and alertness by stimulating the release of dopamine, serotonin, and norepinephrine.
- Phenylethylamine may act on receptors such as trace amine-associated receptors (TAARs), and it can influence the release of neurochemicals that regulate mood and energy levels.
3. Effects
Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA):
- Anti-inflammatory: Effective in reducing inflammation, particularly in conditions like chronic pain, neuropathy, and autoimmune diseases.
- Analgesic: Used for pain relief in conditions such as fibromyalgia, osteoarthritis, and neuropathic pain.
- Neuroprotective: Shows promise in supporting brain health, possibly benefiting those with neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Phenylethylamine (PEA):
- Mood Enhancement: Known for its “euphoric” effects and is sometimes referred to as the “love molecule” due to its association with feelings of love and happiness.
- Cognitive Boost: Can increase alertness and improve focus.
- Energy and Motivation: By stimulating dopamine release, Phenylethylamine can give an energy boost and increase motivation.
- Appetite Suppression: Some studies suggest Phenylethylamine may reduce appetite, potentially useful in weight management.

4. Clinical Applications
Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA):
- Often used as a supplement for chronic pain, inflammation, and nerve-related issues (e.g., neuropathic pain, multiple sclerosis).
- Investigated for its potential role in treating anxiety and neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease.
Phenylethylamine (PEA):
- Sometimes marketed as a mood enhancer, used for mental clarity, focus, and energy.
- Found in some weight loss and cognitive-enhancement supplements due to its stimulant properties.
- Associated with some antidepressant effects but typically not as potent or long-lasting as prescription antidepressants.
5. Side Effects
Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA):
- Generally considered safe with few side effects. Some may experience mild gastrointestinal discomfort, but adverse effects are rare.
- Long-term safety data is still being investigated.
Phenylethylamine (PEA):
- Can cause headaches, nausea, and mood swings in some individuals, especially when taken in large doses.
- Some may experience a “crash” after the effects wear off, due to its impact on neurotransmitter release.
- As a mild stimulant, it can increase heart rate and blood pressure in sensitive individuals.
6. Summary Comparison
Palmitoylethanolamide (PEA): More focused on anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective benefits, useful for pain management, inflammation, and supporting brain health.
Phenylethylamine (PEA): Primarily known for its mood-enhancing and stimulating effects, contributing to mental clarity, alertness, and euphoria.
Conclusion
Both compounds are beneficial in different contexts. Palmitoylethanolamide is mainly used for its anti-inflammatory and pain-relieving effects, whereas phenylethylamine is primarily used for its mood-boosting and stimulating properties.
