Phycocyanin and phycoerythrin are both types of phycobiliproteins—water-soluble proteins that bind pigments called phycobilins, which are responsible for the color in certain types of algae and cyanobacteria. These proteins play key roles in light harvesting for photosynthesis. While both phycocyanin and phycoerythrin are found in different organisms, they differ in several aspects:
1. Color:
Phycocyanin: Appears blue due to the phycocyanobilin pigment. It is primarily found in cyanobacteria, some red algae, and certain species of green algae.
Phycoerythrin: Appears red to pink, owing to the phycoerythrobilin pigment. It is commonly found in red algae and some cyanobacteria.
2. Absorption Spectrum:
Phycocyanin: Absorbs light primarily in the orange-red and red regions (around 620-650 nm) of the visible spectrum, with peaks typically around 620 nm and 650 nm.
Phycoerythrin: Absorbs light in the blue and green regions (around 500-570 nm), with peaks around 545-570 nm.
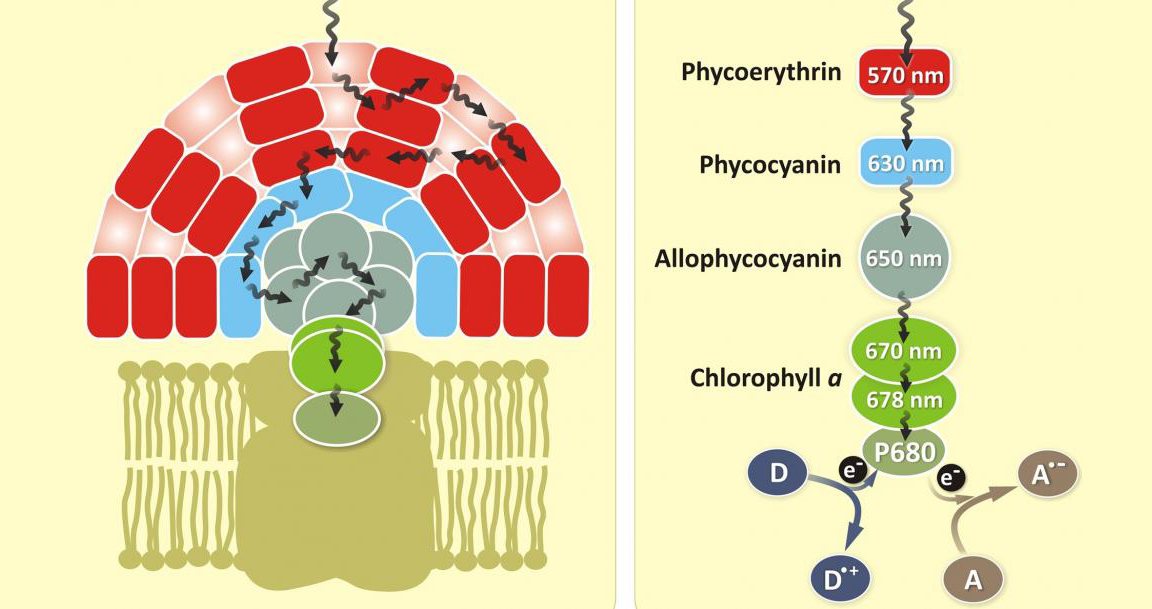
3. Function:
Both phycocyanin and phycoerythrin serve as light-harvesting complexes that collect light energy and transfer it to the photosynthetic reaction centers, where it is used to drive photosynthesis.
Phycocyanin tends to absorb light more efficiently in the red and orange wavelengths, whereas phycoerythrin is better at capturing light in the green and blue wavelengths. This difference helps algae and cyanobacteria maximize light absorption across different environmental conditions.
4. Occurrence:
Phycocyanin is most commonly found in cyanobacteria (such as Spirulina) and blue-green algae, as well as some red algae.
Phycoerythrin is found primarily in red algae and some cyanobacteria that grow in deeper, dimmer environments where they need to absorb more of the available light.
5. Applications:
Phycocyanin is used in various industries due to its natural colorant properties. It is commonly used as a blue food coloring (E6), in cosmetics, and in the nutraceutical industry as a dietary supplement due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties.
Phycoerythrin is also used as a fluorescent probe in biological research, especially in flow cytometry and immunoassays, because of its bright red fluorescence when excited by certain wavelengths of light.
6. Structural Differences:
Both are globular proteins, but they have different chromophore-binding sites and different structures suited to their specific absorption characteristics.
Phycocyanin is composed of alpha and beta subunits, with each subunit containing a phycocyanobilin chromophore, whereas phycoerythrin consists of alpha and beta subunits as well, but they bind phycoerythrobilin chromophores.
Summary of Key Differences:
| Characteristic | Phycocyanin | Phycoerythrin |
| Color | Blue (due to phycocyanobilin) | Red (due to phycoerythrobilin) |
| Absorption Peak | 620–650 nm (red-orange light) | 545–570 nm (blue-green light) |
| Occurrence | Cyanobacteria, some red algae | Red algae, some cyanobacteria |
| Function | Light harvesting in photosynthesis | Light harvesting in photosynthesis |
| Applications | Food coloring, supplements, cosmetics | Fluorescent probes, research, food coloring |
| Chromophore | Phycocyanobilin | Phycoerythrobilin |
Both phycocyanin and phycoerythrin are essential for their respective organisms, aiding in efficient light absorption and enabling them to thrive in their specific ecological niches.
