Bacillus Megaterium is a species of gram-positive, endospore-forming bacterium found in various environments, including soil, water, and decaying plant material. It has gained significant interest in biotechnology and industrial applications due to its ability to produce various enzymes, metabolites, and other valuable compounds.
The processing of Bacillus Megaterium typically involves the following steps:
1.Isolation and Cultivation: To begin processing Bacillus Megaterium, it is first isolated from its natural environment. Soil samples, compost, or other suitable sources may be used for isolation. The bacterium is then cultured on appropriate agar plates or in liquid media to allow its growth and proliferation.
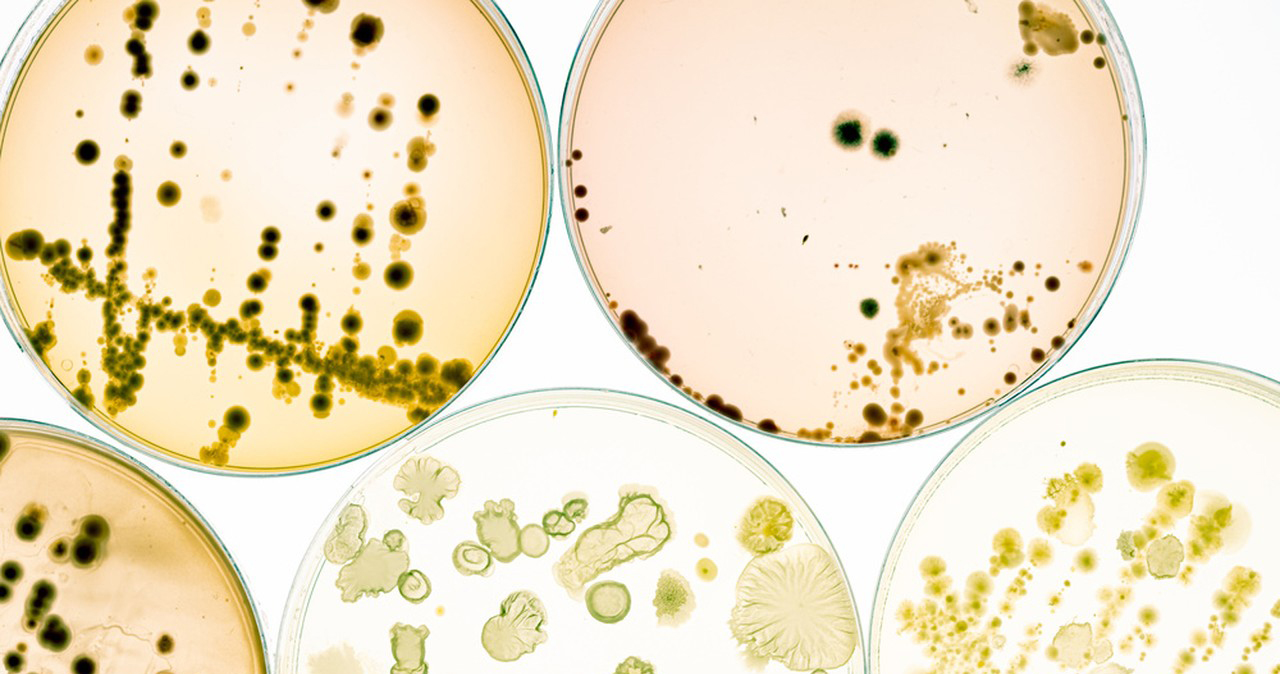
2.Strain Selection: After isolation, different Bacillus Megaterium strains may be screened for specific desirable traits or abilities. Strains with the highest yield of the target product or enzyme of interest may be selected for further processing.
3.Scaling-Up: Once a suitable strain is selected, the cultivation process is scaled up from laboratory flasks or plates to larger bioreactors. This allows for the mass production of Bacillus Megaterium and the target product.
4.Fermentation: Fermentation is a crucial step in processing Bacillus Megaterium. It involves providing the bacteria with optimal conditions for growth and production. Key parameters include temperature, pH, oxygen levels, and nutrient supply. During fermentation, Bacillus Megaterium may produce enzymes, metabolites, or other valuable compounds that are secreted into the fermentation broth.
5.Harvesting: After the fermentation process is completed, the bacterial cells and the target product are harvested from the fermentation broth. Various methods can be employed for cell separation, including centrifugation, filtration, or other solid-liquid separation techniques.
6.Purification: The harvested product is often a mixture of the target compound and other cellular components. Therefore, purification is necessary to isolate and concentrate the desired product. Different purification techniques, such as chromatography or filtration, may be used depending on the nature of the target compound.
7.Formulation and Packaging: Once the target product is purified, it may be further processed to form a final product suitable for commercial use. This can involve formulating the product into specific formulations or packaging it for distribution and storage.
Applications of Bacillus Megaterium in biotechnology can vary widely and include the production of enzymes (e.g., proteases, amylases, lipases), bioactive compounds, biofertilizers, and probiotics, among others.
It’s important to note that the specific processing steps may vary depending on the intended product and the industry application of Bacillus Megaterium. Additionally, adherence to Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and other quality control measures is essential to ensure the production of safe and high-quality products.
