Sialic Acid(N-Acetylneuraminic Acid)
Sialic acid (N-Acetylneuraminic Acid, or Neu5Ac) is a naturally occurring nine-carbon sugar found at the terminal positions of glycoproteins and glycolipids in animal cells.
Description

| Product Name | Sialic Acid(N-Acetylneuraminic Acid) |
| Appearance | White Powder |
| Specs Available | 99% |
| CAS NO. | 131-48-6 |



Sialic Acid(N-Acetylneuraminic Acid) is a generic term for the N- or O-substituted derivatives of neuraminic acid, a monosaccharide with a nine-carbon backbone.
It is also the name for the most common member of this group, N-acetylneuraminic acid (Neu5Ac or NANA). Sialic acids are found widely distributed in animal tissues and to a lesser extent in other organisms, ranging from fungi to yeasts and bacteria, mostly in glycoproteins and gangliosides (they occur at the end of sugar chains connected to the surfaces of cells and soluble proteins).

1. Sialic Acid(N-Acetylneuraminic Acid): Sialic Acid(N-Acetylneuraminic Acid) is a derivative of a 9-carbon monosaccharide. The name comes from the Greek σιαλοσ (sialos) ‘saliva’.
2. This is a negatively charged ion that gives the saliva a smooth feel.
3. It is not only based on the role of “inducing” invading pathogens, but is currently recognized as a transmitter of gangliosides and is a component of the brain.
4. Sialic Acid(N-Acetylneuraminic Acid) can prevent the invasion of germs.
5. Sialic Acid(N-Acetylneuraminic Acid) is also a receptor for influenza viruses, and is a binding site for influenza viruses to bind to mucous cells.








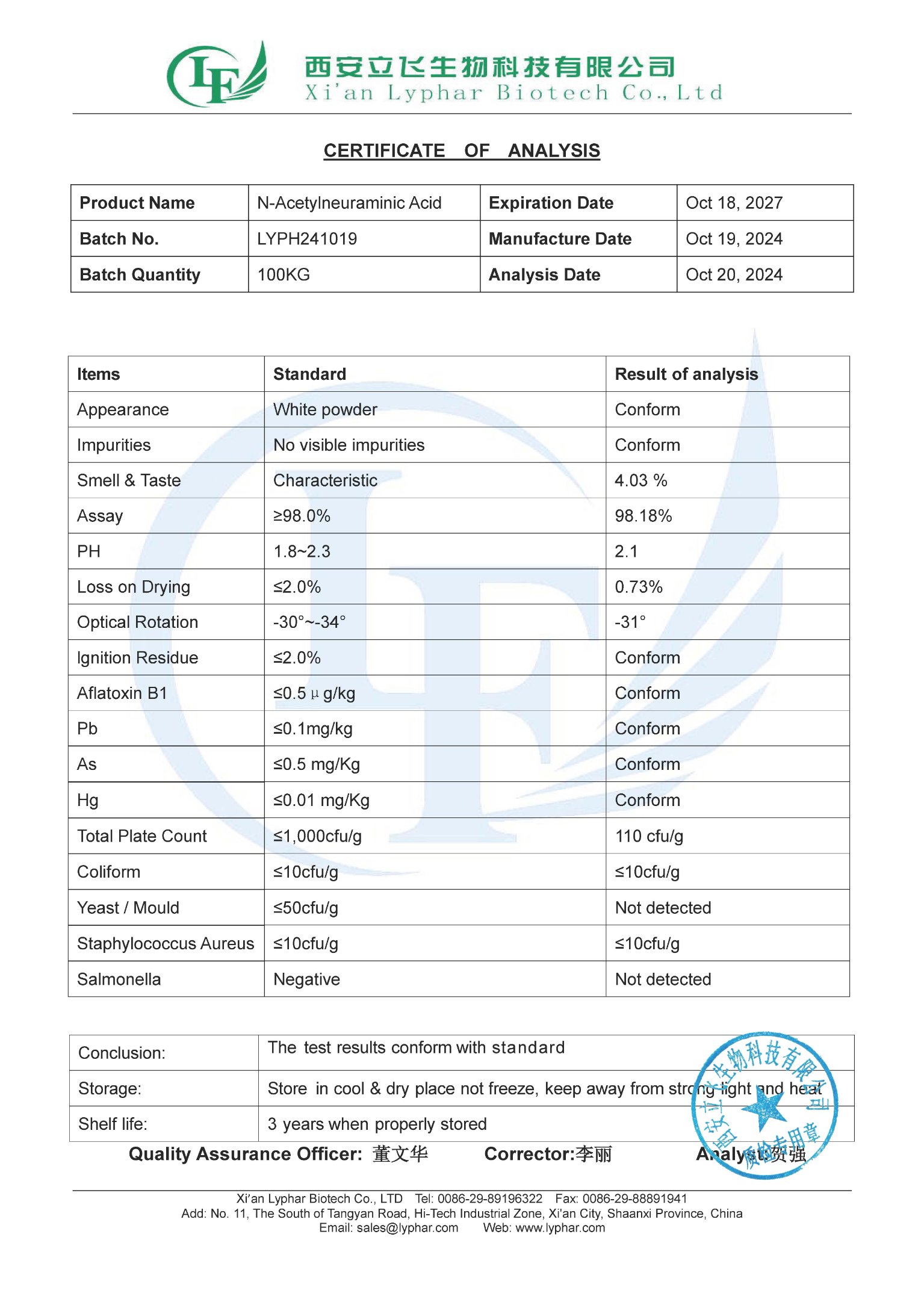
Test Report