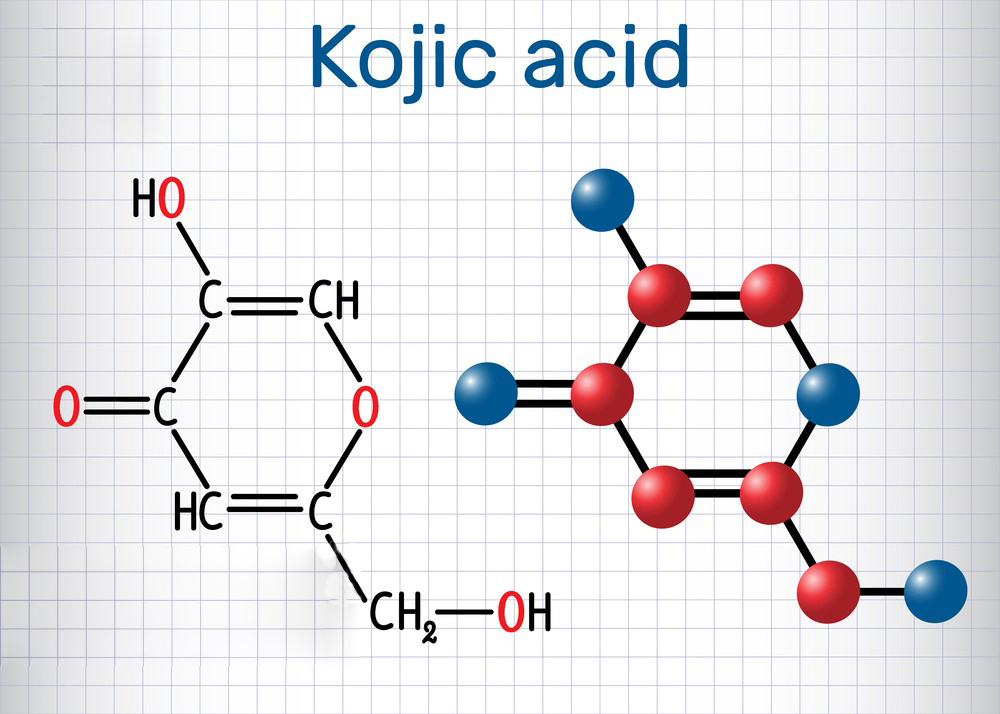
Kojic acid (KA) is a naturally occurring organic compound, most notably derived from certain fungi and produced as a byproduct of fermentation processes. It has been widely studied due to its diverse biological activities, particularly in skin care and pharmaceutical applications. The main research directions involving kojic acid include:
1. Skin Whitening and Pigmentation
Kojic acid is well known for its ability to inhibit melanin production, making it a popular agent in skin lightening products. Research in this area is focused on:
- Mechanisms of action: Kojic acid inhibits the activity of tyrosinase, an enzyme responsible for the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. Studies continue to explore how it interacts with tyrosinase and other enzymes involved in melanogenesis.
- Formulation optimization: Research is aimed at improving the stability and efficacy of kojic acid in cosmetic products, as it tends to degrade in the presence of light and air.
- Combination therapies: Kojic acid is often studied in combination with other skin-lightening agents, like Vitamin C, hydroquinone, or niacinamide, to enhance effectiveness and minimize side effects.

2. Antioxidant and Anti-inflammatory Properties
Kojic acid also exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, which are relevant to its potential use in treating skin aging, inflammation, and other dermatological conditions. Researchers are investigating:
- Cellular protection: The ability of kojic acid to scavenge free radicals and reduce oxidative stress, which may help in protecting skin cells from UV-induced damage, aging, and other environmental stressors.
- Anti-inflammatory effects: Research is looking into how kojic acid might mitigate inflammatory responses, which could be useful in treating conditions like acne or rosacea.
3. Antimicrobial and Antifungal Properties
Kojic acid has been reported to possess antimicrobial and antifungal properties, making it a potential agent for:
- Topical treatments for fungal infections: Kojic acid’s antifungal activity is being explored for use in treating skin infections caused by fungi like Candida or Dermatophytes.
- Acne management: Its antimicrobial properties can contribute to acne treatment by targeting Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes), the bacteria implicated in acne development.
4. Anti-cancer Activity
Some studies suggest that kojic acid may have anti-cancer potential due to its ability to inhibit certain enzymes involved in carcinogenesis, such as tyrosinase, which is also involved in the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Current research includes:
- Inhibition of cancer cell growth: Studies focus on how kojic acid may affect the proliferation and apoptosis (programmed cell death) of various cancer cell lines.
- Mechanisms of action: Investigating how kojic acid can modulate signaling pathways associated with cancer cell growth and metastasis.
5. Neuroprotective Effects
There is growing interest in the potential neuroprotective effects of kojic acid, especially its ability to protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s disease. Research in this area looks at:
- Oxidative stress in neurodegeneration: Investigating whether kojic acid’s antioxidant properties can reduce oxidative stress in brain cells, which is a key factor in neurodegenerative diseases.
- Neuroprotection in cell models: Kojic acid is impact on neurotoxicity in cell cultures, particularly in relation to diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s.
6. Food and Pharmaceutical Industry Applications
Kojic acid is also used in food preservation due to its antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Additionally:
- Preservative in cosmetics: Kojic acid has been investigated as a natural preservative in cosmetics and skin care products to prevent microbial contamination and extend shelf life.
- Synthetic biology for production: Advances in synthetic biology and biotechnological processes are being used to enhance kojic acid production via microbial fermentation, improving yields and cost-effectiveness.
7. Toxicity and Safety Studies
While kojic acid is considered relatively safe for topical use, concerns about potential side effects (such as skin irritation, allergic reactions, or cytotoxicity) remain. Ongoing studies focus on:
- Safety in long-term use: Evaluating the long-term safety of kojic acid in skincare and cosmetics, especially when used at higher concentrations.
- Regulatory standards: Monitoring kojic acid’s safety profile and determining acceptable concentrations for various cosmetic and pharmaceutical formulations.
8. Sustainability and Green Chemistry
Research into sustainable production methods for kojic acid is also gaining traction. This includes:
- Microbial fermentation and biotechnology: Exploring more environmentally friendly, efficient, and cost-effective methods of kojic acid production using engineered microorganisms.
- Alternative sources: Investigating alternative natural sources of kojic acid, such as certain mushrooms, rice, and other fungi.
Summary
Kojic acid continues to be a compound of significant interest across diverse research fields, particularly in skin care, pharmaceuticals, and biotechnology. Its roles in pigmentation regulation, antioxidant properties, and potential anti-cancer or neuroprotective effects open doors to numerous applications. Ongoing studies focus on maximizing its benefits while minimizing potential side effects and improving its production and stability.
