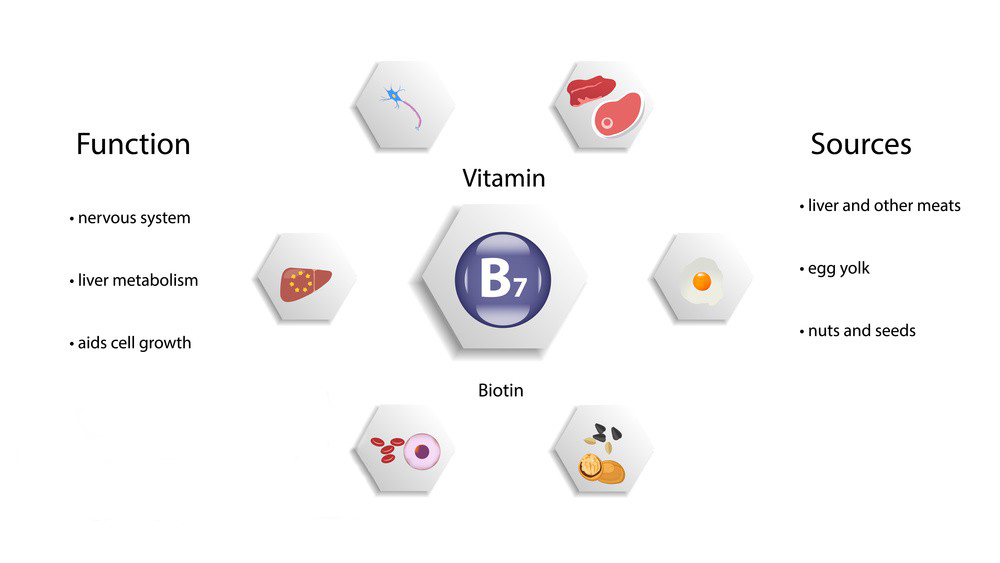
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H, is a water-soluble B-vitamin that plays a crucial role in various metabolic processes in the body. It is often promoted for its potential benefits on hair, skin, and nails, as well as its role in supporting healthy metabolism and nerve function. Biotin is commonly found in foods like eggs, nuts, seeds, and certain vegetables.
Some people take biotin supplements to address specific concerns, such as hair thinning, brittle nails, and skin issues. However, the scientific evidence supporting the effectiveness of biotin for these purposes is limited and mixed. Here’s what’s known based on available research:
- Hair Health: Biotin is often associated with promoting healthy hair growth and preventing hair loss. Some studies have suggested a possible link between biotin deficiency and hair loss. However, more research is needed to establish a clear and direct connection. Biotin supplementation might be helpful for individuals with biotin deficiency, but its effectiveness for general hair health is still debated.
- Nail Health: Biotin is sometimes recommended to improve the strength and health of nails. Limited research suggests that biotin supplementation might be beneficial for people with brittle nails, particularly those with biotin deficiency. However, results are not consistent across all studies, and more research is required to confirm these effects.
- Skin Health: Biotin is involved in maintaining healthy skin, and deficiencies may lead to skin problems. Some studies have suggested that biotin supplementation could help improve certain skin conditions. However, the evidence is not yet robust enough to draw firm conclusions.
- Metabolism and Blood Sugar: Biotin is involved in the metabolism of carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. Some research has indicated that biotin supplementation might have a positive impact on glucose metabolism and blood sugar control, particularly in individuals with type 2 diabetes. However, more high-quality studies are needed to confirm these potential effects.
- Nerve Function: Biotin plays a role in maintaining healthy nerve function. Biotin deficiency can lead to neurological symptoms, such as numbness and tingling in the extremities. Biotin supplementation may help alleviate these symptoms in cases of deficiency.
It’s important to note that while biotin supplements are generally considered safe when taken at recommended doses, very high doses (megadoses) of biotin can potentially interfere with certain lab tests, leading to inaccurate results.
Before starting any supplement, including biotin, it’s recommended to consult with a healthcare professional. They can help determine if you have a biotin deficiency or if supplementation is appropriate for your specific health concerns. Keep in mind that individual responses to supplements can vary, and more research is needed to fully understand the potential benefits and risks of biotin supplementation.
Efficacy evaluation of Biotin
Biotin, also known as vitamin B7 or vitamin H, is a water-soluble B-vitamin that plays a crucial role in various metabolic processes in the body. It is often promoted for its potential benefits in improving the health of hair, skin, and nails, as well as supporting energy metabolism. However, it’s important to note that scientific evidence regarding the efficacy of biotin supplementation for these purposes is somewhat limited and mixed.
Here is an overview of some of the potential benefits of biotin and the current state of its efficacy evaluation:
- Hair Health: Biotin is often marketed as a supplement that can improve hair health, promote hair growth, and prevent hair loss. While biotin deficiency can lead to hair problems, there is limited scientific evidence to support the claim that biotin supplementation can significantly impact hair growth or hair quality in individuals who are not deficient in biotin. The evidence is generally anecdotal or based on small studies with mixed results.
- Skin Health: Biotin is sometimes recommended for improving the health of the skin, including addressing issues like dry skin, rashes, and acne. However, scientific studies linking biotin supplementation directly to skin health improvements are lacking. Most skin conditions are influenced by a variety of factors, and it’s important to consult a dermatologist for appropriate treatment.
- Nail Health: Similar to hair and skin, biotin has been suggested to enhance the strength and quality of nails. Some studies have shown a potential benefit of biotin supplementation in improving brittle nails, particularly in individuals with biotin deficiency. However, more research is needed to establish a clear link between biotin supplementation and nail health.
- Metabolic Functions: Biotin is involved in energy metabolism and the breakdown of macronutrients like carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It is an essential coenzyme in various enzymatic reactions. Biotin deficiency can lead to symptoms like fatigue, muscle pain, and cognitive impairments. However, in well-nourished individuals, the need for biotin supplementation to support these metabolic functions is generally not established.
- Biotin Deficiency and Medical Conditions: Biotin deficiency is rare and is usually associated with certain medical conditions or medications that interfere with its absorption. In such cases, biotin supplementation can be effective in addressing deficiency-related symptoms. Biotin supplements are often prescribed for individuals with biotinidase deficiency, a rare inherited disorder.
It’s important to approach biotin supplementation with caution. While biotin is generally considered safe at recommended doses, taking excessive amounts of biotin supplements can lead to potential adverse effects and may interfere with laboratory tests, such as those used for thyroid function testing.
If you are considering using biotin supplements for any specific health concern, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before starting supplementation. They can help determine if you have a genuine deficiency, provide guidance on appropriate dosages, and offer alternative treatments if necessary. As with any supplement, a balanced and varied diet remains the best approach to obtaining essential nutrients, including biotin.
