Sericin and silk fibroin are two primary proteins found in silk. They serve different functions and have distinct properties. Here’s a comparison:
1. Origin and Structure
Sericin:
- A glue-like protein that surrounds and binds silk fibroin filaments.
- Composed of a high proportion of polar amino acids, such as serine, aspartic acid, and glycine.
- Soluble in water and heat-sensitive.
Silk Fibroin:
- The core structural protein of silk, forming the silk thread’s primary fibers.
- Composed primarily of non-polar amino acids like glycine, alanine, and serine, arranged in β-sheet structures.
- Insoluble in water and highly durable.

2. Physical Properties
- Amorphous and hydrophilic (water-attracting).
- Exhibits lower mechanical strength and elasticity.
- Acts as a natural adhesive.
Silk Fibroin:
- Crystalline and hydrophobic (water-repelling).
- Provides high tensile strength, elasticity, and resilience.
- Responsible for silk’s mechanical properties and luster.
3. Functions in Silk Production
- Protects fibroin during the spinning process and helps form the cocoon.
- Removed during the degumming process to make silk smoother.
Silk Fibroin:
- Forms the structural backbone of silk fibers.
- Remains intact after the degumming process to produce lustrous silk threads.
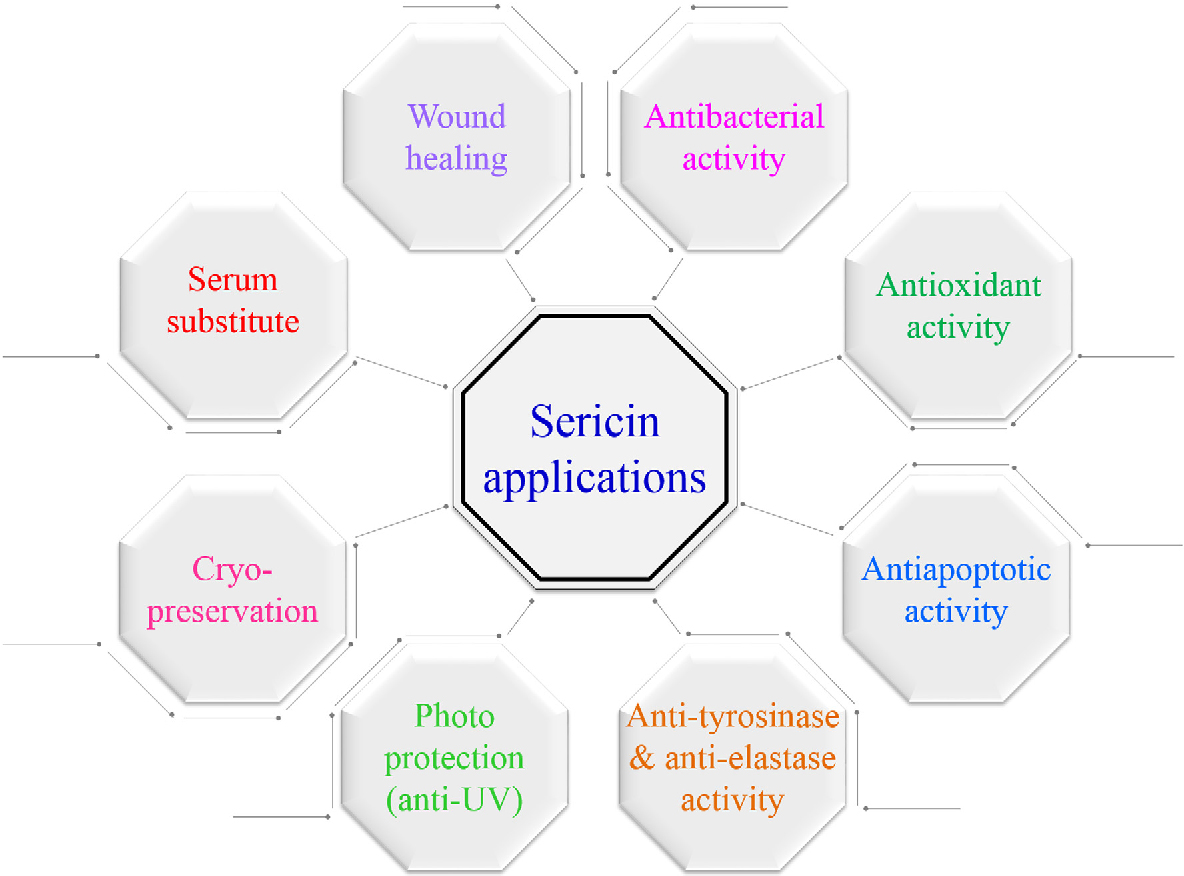
4. Applications
Sericin:
- Used in cosmetics due to its moisturizing and antioxidant properties.
- Utilized in biomedical fields for wound healing, tissue engineering, and drug delivery.
- Serves as a coating material due to its biocompatibility.
Silk Fibroin:
- Applied in textiles for producing high-quality fabrics.
- Widely used in biomedicine for sutures, scaffolds, and drug delivery systems.
- Acts as a substrate for tissue engineering due to its mechanical strength and biodegradability.
5. Environmental Impact
- Often discarded as waste during silk processing, raising environmental concerns. However, recycling and repurposing are increasing.
Silk Fibroin:
- Considered eco-friendly when used sustainably, with minimal waste during processing.
Summary
- Sericin is a hydrophilic, adhesive protein with biomedical and cosmetic applications.
- Silk fibroin is a hydrophobic, structural protein vital for textile and medical applications.
Their complementary properties make them both valuable, but they serve vastly different roles.
