NMN (Nicotinamide mononucleotide) is a nucleotide derived from nicotinamide, a form of vitamin B3 (niacin). It has become popular as a supplement due to its role as a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a vital molecule involved in cellular metabolism, energy production, and aging. The synthesis of NMN can be done through various methods, primarily chemical or enzymatic approaches. Here’s a general overview of the synthesis process:
Chemical Synthesis of NMN
The chemical synthesis of NMN involves several steps to combine nicotinamide with ribose (a sugar molecule) and a phosphate group. One general route involves:
1.Synthesis of the Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) Intermediate:
- Ribose (in its D-configuration) is first activated to facilitate the attachment of nicotinamide.
- This step may involve protecting group strategies to ensure selectivity and avoid unwanted reactions.
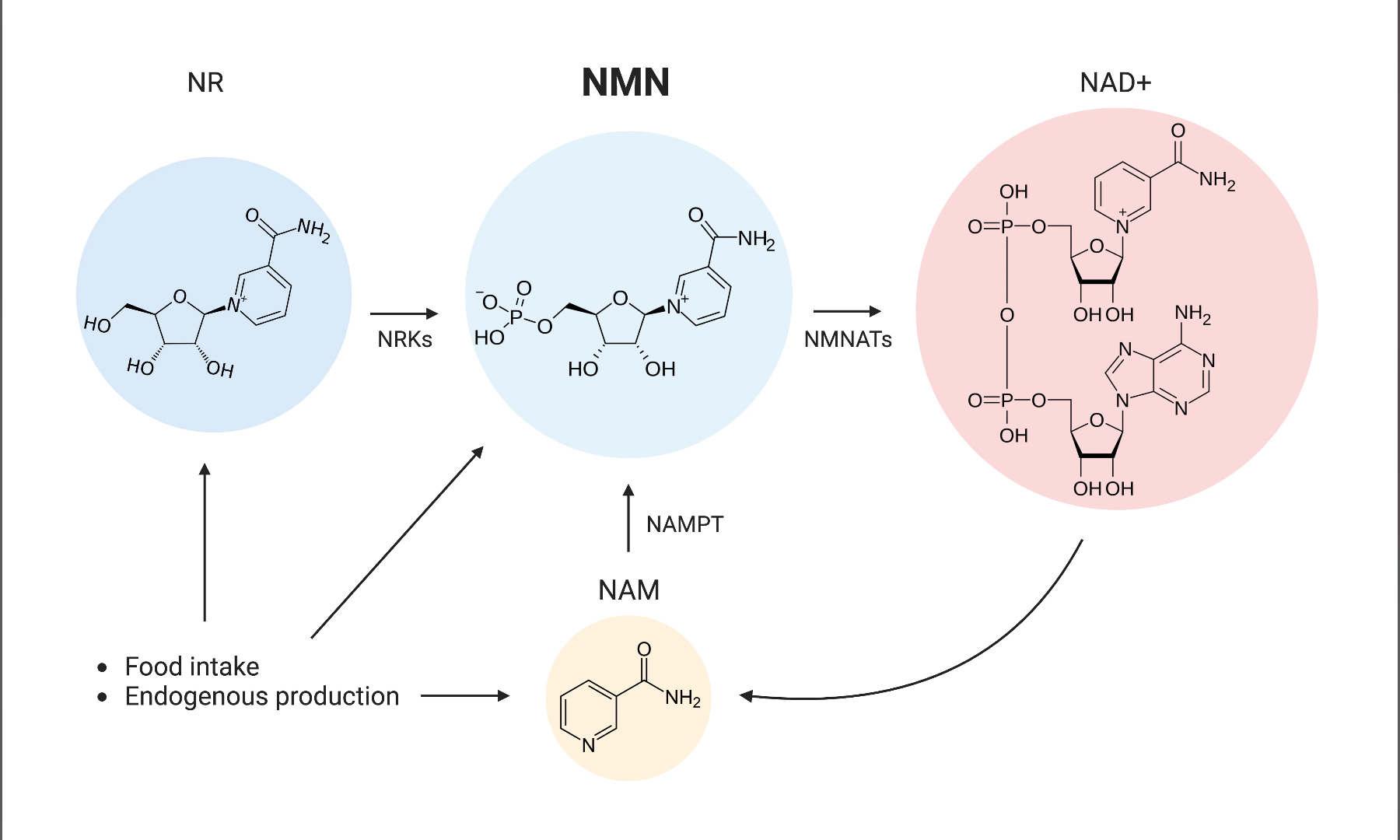
2.Attachment of Nicotinamide:
- The nicotinamide group is typically linked to the ribose backbone through a glycosidic bond.
- This reaction can be catalyzed by an appropriate catalyst or conducted under suitable conditions to ensure the formation of the correct intermediate.
3.Phosphorylation of Nicotinamide Riboside (NR):
- The final step involves the phosphorylation of nicotinamide riboside at the 5′-hydroxyl group, converting it into NMN.
- This is typically done using phosphorylating agents like ATP or other phosphate donors in the presence of a kinase enzyme or chemical catalysts.
4.Purification:
- After synthesis, the product is purified, often using techniques such as column chromatography, crystallization, or recrystallization.
Key Enzymes Involved
- NMNAT (Nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase): This enzyme catalyzes the transfer of the adenylyl group from ATP to nicotinamide, producing NMN and releasing pyrophosphate.
- NAD+ biosynthesis pathway enzymes: These enzymes are involved in the conversion of precursors like nicotinic acid and nicotinamide into NAD+ and NMN.

Summary of Key Steps in Both Approaches:
- Activation of Ribose (for chemical synthesis) or use of PRPP (for enzymatic synthesis).
- Attachment of Nicotinamide to ribose.
- Phosphorylation to form NMN.
- Purification of the final product.
Chemical methods may require more complex reagents and conditions, while enzymatic methods can be more selective and environmentally friendly, albeit requiring enzyme isolation or expression systems.
The demand for NMN has led to increasing interest in both scalable chemical and enzymatic synthesis methods to meet market needs, particularly for use as a dietary supplement.
