Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is a compound that belongs to the vitamin B3 family, and it is often used as a dietary supplement due to its potential health benefits, particularly in the context of cellular energy production and longevity. The basic components of nicotinamide riboside are:
Nicotinamide: Nicotinamide is a form of vitamin B3 (niacin) and serves as the core structural component of nicotinamide riboside.
Ribose: Ribose is a type of sugar molecule (a pentose sugar) that is attached to the nicotinamide molecule in nicotinamide riboside. This ribose-nicotinamide combination gives rise to the name “nicotinamide riboside.”
Phosphate Group: In some forms of nicotinamide riboside, a phosphate group may also be attached to the ribose molecule. When a phosphate group is added, it forms a molecule known as nicotinamide riboside phosphate (NRP), which can have specific roles in various biochemical processes.
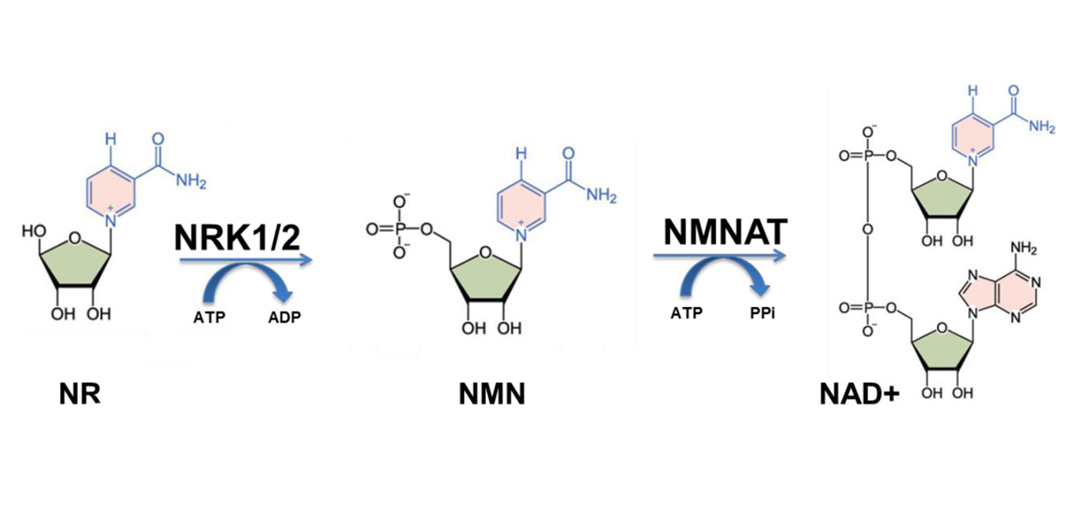
Nicotinamide riboside is a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a coenzyme that plays a critical role in various cellular processes, including energy metabolism and DNA repair. By providing a source of nicotinamide, which can be converted into NAD+ in the body, nicotinamide riboside is believed to support these cellular functions and potentially offer health benefits. It is commonly used as a dietary supplement to boost NAD+ levels, which tend to decline with age. However, more research is needed to fully understand its effects and potential therapeutic applications.
Applications of Nicotinamide Riboside
Nicotinamide Riboside (NR) is a form of vitamin B3, also known as niacin or nicotinic acid, that has gained attention for its potential health benefits, particularly in the field of aging and longevity research. NR is a precursor to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+), a coenzyme involved in various cellular processes, including energy production, DNA repair, and gene regulation. Here are some of the potential applications of nicotinamide riboside:
Aging and Longevity: NR has been studied for its potential to slow down the aging process and extend lifespan. NAD+ levels tend to decline with age, and NR supplementation may help boost NAD+ levels, which can support cellular repair and energy production. While research is ongoing, some studies in animals and early-stage human trials have shown promising results.
Metabolic Health: Nicotinamide riboside has been investigated for its role in improving metabolic health. It may help regulate blood sugar levels, reduce insulin resistance, and improve mitochondrial function. These effects could have implications for conditions like type 2 diabetes and obesity.
Neurological Health: Some research suggests that NR supplementation may support brain health. NAD+ is involved in neural repair mechanisms, and NR could potentially help protect against neurodegenerative diseases like Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease. More research is needed in this area.
Cardiovascular Health: NR may have potential benefits for heart health. It could help improve blood vessel function and reduce the risk of heart disease. By supporting NAD+ levels, NR might also help in the repair of damaged DNA in cells within the cardiovascular system.

Exercise Performance: Nicotinamide riboside has been investigated as a potential supplement for athletes and individuals looking to enhance exercise performance. By boosting NAD+ levels, NR may improve mitochondrial function and energy production, potentially leading to increased endurance and muscle recovery.
Skin Health: Some studies suggest that NR may protect against UV radiation-induced skin damage and promote skin health by supporting cellular repair mechanisms.
DNA Repair: NR’s role in NAD+ synthesis makes it important for DNA repair processes. Maintaining sufficient NAD+ levels may help cells repair DNA damage more effectively, reducing the risk of mutations and cancer.
Weight Management: Nicotinamide riboside may help with weight management by improving metabolic function and increasing energy expenditure. However, more research is needed to establish its effectiveness in this regard.
It’s important to note that while NR shows promise in various areas of health and longevity, more research is needed to fully understand its mechanisms and potential side effects. If you are considering NR supplementation, it’s advisable to consult with a healthcare professional, as individual responses to supplements can vary, and long-term safety and efficacy are still being studied. Additionally, dietary sources of niacin, such as meat, fish, and nuts, can also contribute to NAD+ levels in the body.
