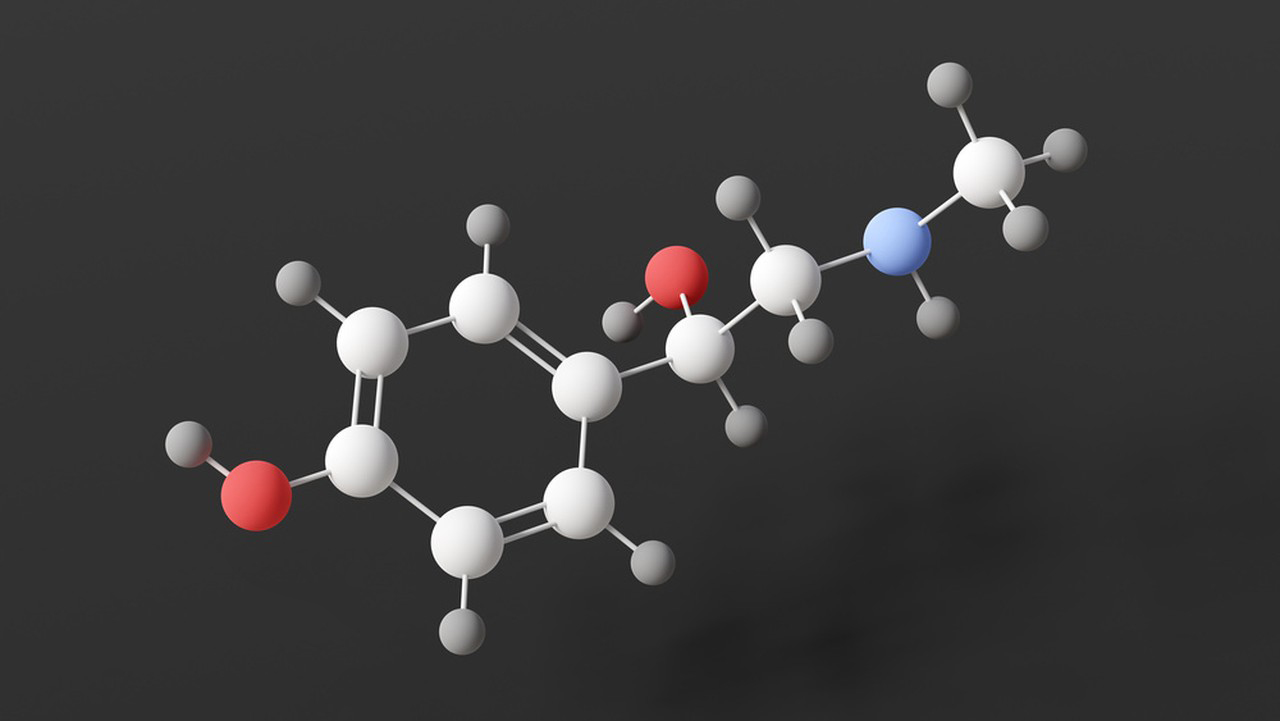
Synephrine is a naturally occurring compound found in some plants, particularly citrus fruits. It is often used in dietary supplements and weight loss products. The basic ingredients of synephrine are derived from these natural sources. The primary source of synephrine is Citrus aurantium, commonly known as bitter orange.
The main components of synephrine include:
1.Bitter Orange Extract (Citrus aurantium): The peel of bitter oranges is rich in synephrine. This extract is commonly used in supplements for its potential thermogenic and appetite-suppressant properties.
2.Octopamine: Synephrine is structurally similar to octopamine, another naturally occurring amine. Octopamine is found in trace amounts in bitter oranges and contributes to the overall effects of synephrine.
3.N-methyltyramine: This is another amine compound that is present in some sources of synephrine, contributing to its pharmacological effects.
It’s important to note that while synephrine is naturally derived, its use in supplements has raised some concerns due to potential health risks. It’s always advisable to consult with a healthcare professional before using any supplements containing synephrine, especially for individuals with pre-existing health conditions or those taking medication.
Efficacy and effects of Synephrine
Synephrine is a naturally occurring compound found in some plants, particularly in the peel of bitter oranges (Citrus aurantium). It has been used for various purposes, including weight loss and athletic performance enhancement. However, it’s important to note that while synephrine has potential effects, its efficacy and safety are subjects of debate.
1.Weight Loss:
Mechanism: Synephrine is believed to stimulate the metabolism and increase calorie expenditure. It is thought to work by interacting with adrenergic receptors, particularly beta-3 receptors, which can lead to increased thermogenesis and fat breakdown.
Efficacy: Research on synephrine’s effectiveness for weight loss is limited and results are mixed. Some studies suggest a modest increase in metabolic rate, while others find no significant effects.
2.Athletic Performance:
Mechanism: Synephrine may have stimulant effects, potentially improving alertness, energy levels, and endurance.
Efficacy: Evidence on its effectiveness for enhancing athletic performance is also inconclusive. Some studies report improvements in exercise performance, while others find no significant benefits.
3.Safety Concerns:
Cardiovascular Effects: Synephrine can increase heart rate and blood pressure. Individuals with pre-existing cardiovascular conditions should exercise caution.
Interactions: It may interact with medications, particularly those affecting blood pressure and heart function.
Adverse Effects: Some people may experience side effects such as jitteriness, headaches, and gastrointestinal discomfort.
4.Regulatory Status:
In some regions, dietary supplements containing synephrine have faced regulatory scrutiny due to concerns about safety and lack of well-established efficacy.
5.Dosage and Form:
The efficacy and safety of synephrine can be influenced by the form and dosage. Different supplements may contain varying concentrations of synephrine.
It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional before using synephrine or any dietary supplement, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications. Additionally, considering the regulatory landscape and potential risks, it’s advisable to approach the use of synephrine with caution.
