Advantame is an artificial sweetener and flavor enhancer that is structurally related to aspartame, with some modifications. Here are the details of its chemical structure and physical properties:
Chemical Structure of Advantame
Advantame is a derivative of aspartame, with a vanillin (4-methoxy-3-hydroxybenzaldehyde) moiety added to its structure. Its IUPAC name is:
3-(3-Hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)propyl N-[N-[3-(3-hydroxy-4-methoxyphenyl)propyl]-L-α-aspartyl]-L-phenylalaninate
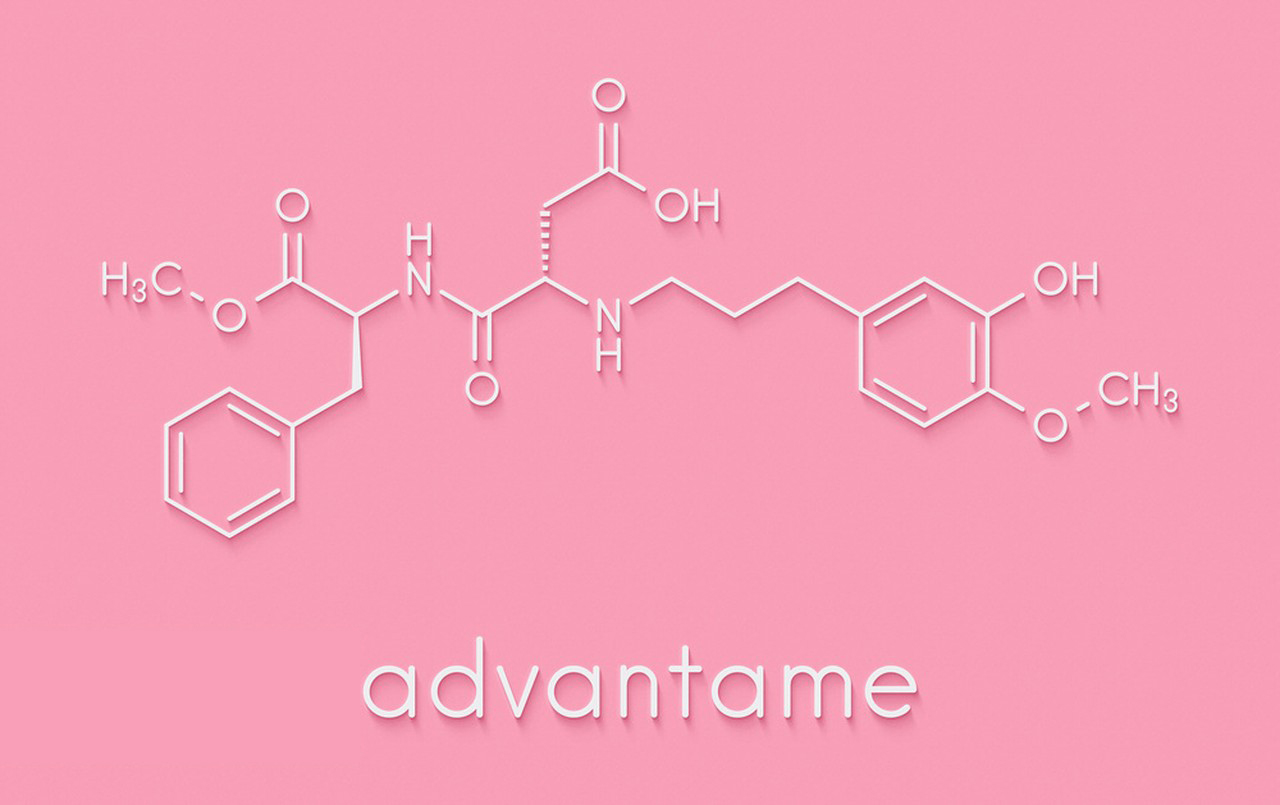
The molecular formula of Advantame is:
C24H30N2O7
Here is the structure:
Aspartame part: C14H18N2O5
Vanillin part: C10H12O3
Physical Properties of Advantame
Molecular Weight: 474.51 g/mol
Appearance: White to off-white powder
Solubility: Advantame is slightly soluble in water and soluble in ethanol.
Stability: It is stable under dry conditions and can be stored at room temperature without significant degradation. However, it is hydrolyzed in acidic or basic solutions.
Sweetness: Advantame is approximately 20,000 times sweeter than sucrose and 100 times sweeter than aspartame, making it one of the most potent artificial sweeteners.
Additional Properties
Melting Point: Advantame decomposes before melting.
Taste Profile: It has a clean, sweet taste with no bitter or metallic aftertaste, making it suitable for a variety of food and beverage applications.

Usage
Advantame is used as a high-intensity sweetener in various food products, including beverages, desserts, and dairy products. It is approved for use in many countries, including the United States, where it is considered safe by the FDA.
In summary, Advantame’s chemical structure and physical properties make it a highly effective and potent artificial sweetener, suitable for a wide range of applications in the food and beverage industry.
