Ceramide is a class of lipids (fats) that play a crucial role in maintaining the health and integrity of the skin’s barrier function. They are a key component of the stratum corneum, which is the outermost layer of the epidermis (the top layer of the skin). Ceramide is essential for maintaining proper hydration, preventing water loss, and protecting the skin from environmental factors. Comprehensive research has been conducted on ceramides to better understand their functions, benefits, and potential applications in skincare and other fields.

Here are some key points from comprehensive research on ceramide:
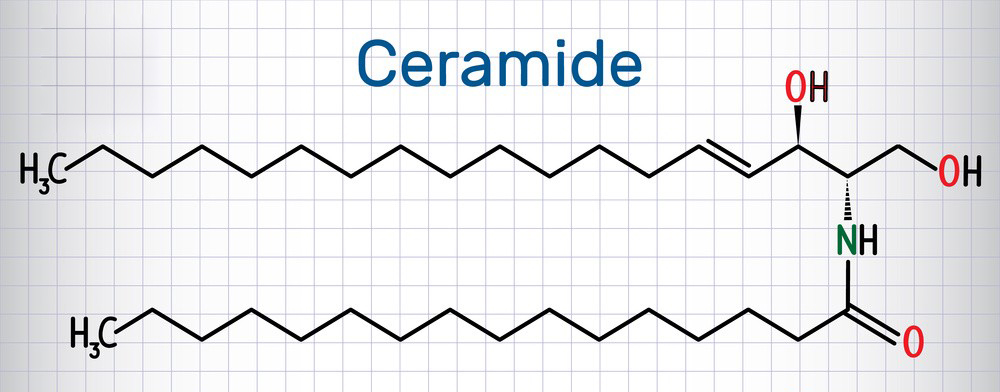
- Structure and Classification: Ceramide is composed of a sphingosine backbone attached to a fatty acid chain. They are classified into different types based on the specific fatty acid chain attached. These classifications include Ceramide 1, Ceramide 2, Ceramide 3, and so on.
- Skin Barrier Function: One of the primary roles of ceramides is to help maintain the skin’s barrier function. They form a protective layer that helps prevent excessive water loss, thus keeping the skin adequately hydrated. A healthy skin barrier also helps protect the skin from environmental aggressors, allergens, and irritants.
- Moisturization: Ceramide is a vital component of moisturizing products and formulations. Research has shown that applying ceramide-containing products topically can help improve skin hydration and alleviate conditions like dry skin, eczema, and psoriasis.
- Skin Disorders: Numerous studies have explored the role of ceramides in various skin disorders. A deficiency in ceramides has been linked to conditions like atopic dermatitis (eczema) and other forms of dermatitis. Researchers are investigating how replenishing ceramides could potentially improve these conditions.
- Aging and Wrinkle Formation: As we age, the levels of ceramides in the skin naturally decrease, contributing to the loss of skin elasticity and the formation of wrinkles. Research suggests that ceramide supplementation in skincare products may help improve skin texture and reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles.
- Wound Healing: Ceramides also play a role in the wound healing process. Studies have shown that ceramides can help accelerate the healing of wounds by promoting cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation.
- Oral Supplementation: In addition to topical applications, researchers have explored the potential benefits of ceramide supplementation through oral consumption. Some studies suggest that oral ceramide supplements may help improve skin hydration and barrier function.
- Ceramides in Skincare: Many skincare products, especially moisturizers and barrier-repairing creams, contain ceramides as key ingredients. These products are often recommended for individuals with dry or sensitive skin, as well as those with compromised skin barriers.
- Future Research: Ongoing research is focused on further understanding the specific roles of different ceramide types, their interactions with other lipids, and their potential applications beyond skincare, such as in pharmaceuticals and biomaterials.
It’s important to note that while ceramides have shown significant potential for improving skin health and addressing various skin concerns, individual responses can vary. If you’re considering using ceramide-containing products or supplements, it’s advisable to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare professional, especially if you have specific skin conditions or concerns.
