Introduction of Jojoba Beads
Jojoba beads are spherical, biodegradable exfoliants made from hydrogenated jojoba oil. They are used primarily in personal care and cosmetic products, particularly in exfoliating scrubs. These beads are an eco-friendly alternative to plastic microbeads, which have been banned in many countries due to their environmental impact.
Origin and Production of Jojoba Beads
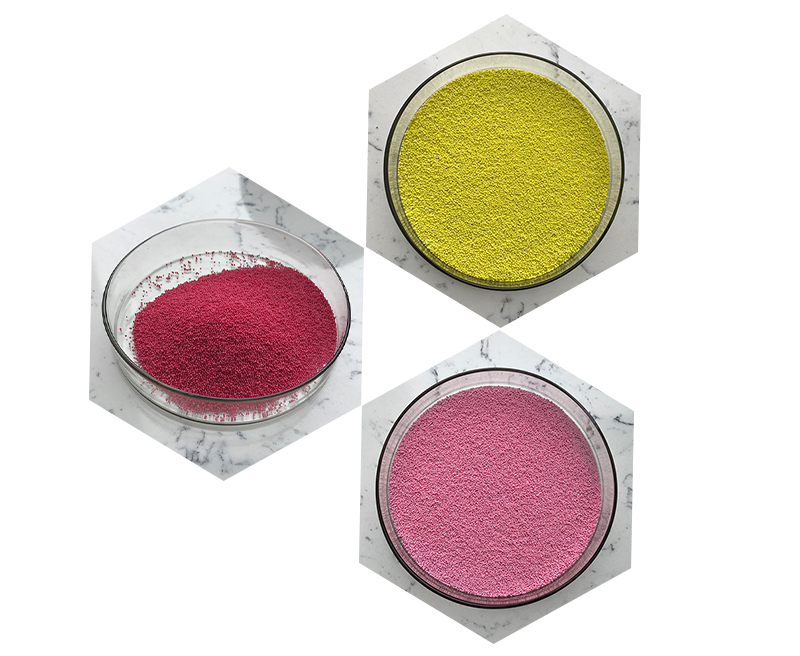
Jojoba (Simmondsia chinensis) is a shrub native to the southwestern United States and northern Mexico. The plant produces seeds rich in a wax ester known as jojoba oil. This oil is hydrogenated to produce jojoba esters, which are then processed into small, uniform beads. These beads come in various sizes and colors, depending on the intended application.

Chemical Composition of Jojoba Beads
Jojoba oil is a liquid wax composed mainly of wax esters, fatty acids, and fatty alcohols. Upon hydrogenation, these components become more stable and form solid jojoba esters. The resulting beads are biodegradable, non-toxic, and gentle on the skin, making them suitable for a wide range of cosmetic formulations.
Applications in Cosmetics of Jojoba Beads
- Exfoliation: Jojoba beads are used in facial and body scrubs to provide gentle exfoliation. Their smooth, round shape reduces the risk of microtears in the skin, making them ideal for sensitive skin.
- Cleansers: They are included in facial cleansers to enhance the removal of dead skin cells and impurities.
- Soaps: Jojoba beads add a mild scrubbing action to soap bars.
- Lip Care: Some lip scrubs use jojoba beads to exfoliate and soften lips.
Benefits of Jojoba Beads
- Biodegradability: Unlike plastic microbeads, jojoba beads are biodegradable and do not contribute to microplastic pollution in aquatic environments.
- Skin-Friendly: They are non-abrasive and less likely to cause irritation compared to harsher exfoliants.
- Versatility: Available in different sizes and colors, they can be customized for various cosmetic products.
- Sustainable: Derived from a renewable resource, jojoba beads support sustainable agricultural practices.
Environmental Impact of Jojoba Beads
The use of jojoba beads in personal care products helps mitigate the environmental issues associated with plastic microbeads. Plastic microbeads, commonly used in exfoliating products, have been found to persist in water bodies, harming marine life and entering the food chain. Jojoba beads, being biodegradable, break down naturally and pose no threat to marine ecosystems.
Market Trends of Jojoba Beads
With growing awareness of environmental sustainability, there is an increasing demand for natural and eco-friendly ingredients in cosmetics. The market for jojoba beads is expanding as more companies reformulate their products to eliminate plastic microbeads.
Research and Development of Jojoba Beads
Ongoing research focuses on optimizing the production process of jojoba beads to enhance their quality and reduce costs. Studies are also exploring new applications of jojoba beads in various cosmetic and dermatological products.
Conclusion of Jojoba Beads
Jojoba beads offer a sustainable and skin-friendly alternative to plastic microbeads in cosmetic products. Their biodegradability, combined with their gentle exfoliating properties, makes them a valuable ingredient in the personal care industry. As environmental regulations become stricter and consumer preferences shift towards eco-friendly products, the use of jojoba beads is expected to grow significantly.
References of Jojoba Beads
Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel. (2008). Safety Assessment of Jojoba Oil and Jojoba Wax. International Journal of Toxicology, 27(S1), 53-63.
Walters, R. M., & Roberts, M. S. (2007). The Role of Permeability Enhancement in Topical Dermatological Formulations. Dermatologic Clinics, 25(2), 137-148.
U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). (2015). Trash-Free Waters: Microplastics. EPA.
