UDCA(Ursodeoxycholic acid) is a bile acid naturally produced by the human body and is also available as a medication. It has been the subject of extensive research due to its various potential therapeutic uses. Below is a comprehensive overview of UDCA and its research findings:
Bile Acid Metabolism: UDCA is a primary bile acid, which means it is synthesized in the liver and contributes to the digestion and absorption of dietary fats. It helps to maintain cholesterol homeostasis and excretion of waste products.
Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC): UDCA is primarily used as a treatment for primary biliary cholangitis (formerly known as primary biliary cirrhosis). PBC is an autoimmune liver disease where the bile ducts in the liver become inflamed and damaged. UDCA has been shown to improve liver function, slow disease progression, and reduce symptoms in patients with PBC.
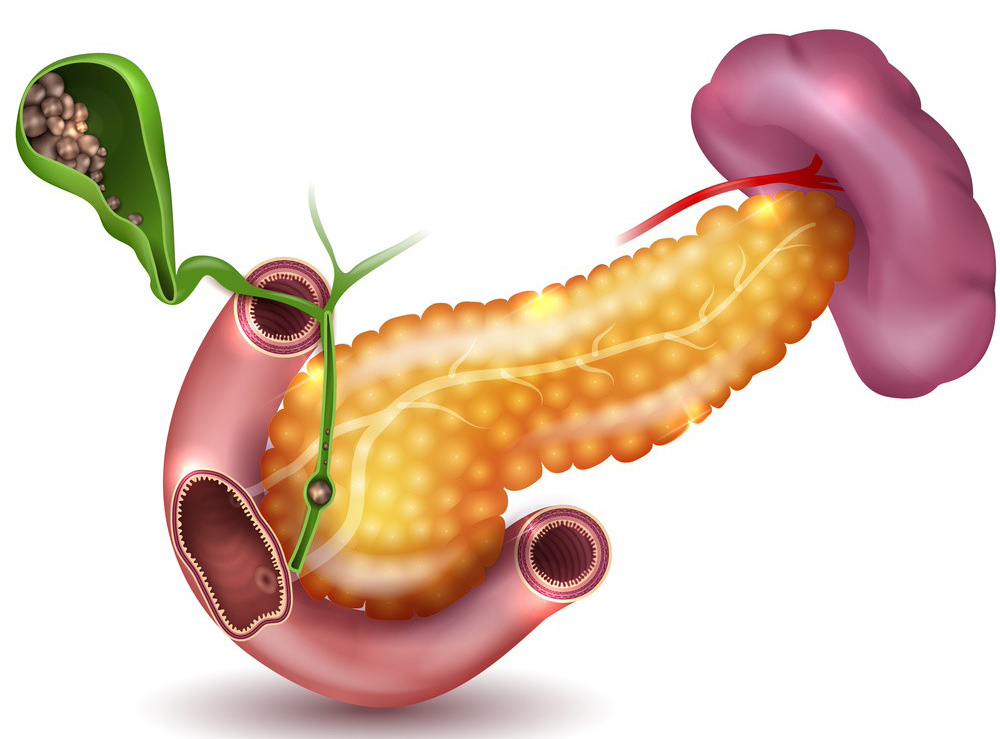
Gallstones: UDCA can be used as a non-surgical treatment for gallstones. It helps dissolve small, radiolucent (non-calcified) cholesterol gallstones in the gallbladder.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Research has suggested that UDCA may have a role in treating NAFLD, a condition characterized by the accumulation of fat in the liver, particularly in cases where inflammation (non-alcoholic steatohepatitis, NASH) is present.
Cystic Fibrosis-Related Liver Disease: UDCA has been investigated as a potential treatment for liver disease associated with cystic fibrosis, a genetic disorder that affects the lungs and digestive system.
Cholestatic Liver Diseases: UDCA is used in the treatment of various cholestatic liver diseases, where bile flow from the liver is reduced or obstructed. It can help improve bile flow and alleviate symptoms in conditions such as primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC) and Alagille syndrome.
Hepatitis C: There is some research into the use of UDCA as an adjunctive therapy for chronic hepatitis C, although its efficacy is still a subject of debate.
Liver Transplantation: UDCA has been used in the management of liver transplant patients, particularly for those with cholestatic liver diseases. It may help improve graft survival and function.
Other Potential Applications: Research is ongoing to explore UDCA’s potential in other conditions, such as certain autoimmune diseases, inflammatory bowel disease, and even neurological disorders.
Safety and Side Effects: UDCA is generally considered safe, but it can have side effects, including diarrhea and, in rare cases, hepatotoxicity. Dosage and monitoring are crucial in its clinical use.
Mechanisms of Action: UDCA’s exact mechanisms of action in various diseases are not fully understood, but it is believed to exert its effects by reducing the cytotoxic effects of other bile acids, modulating the immune system, and influencing lipid metabolism.
Combination Therapies: In some cases, UDCA is used in combination with other medications, such as immunosuppressants or antiviral drugs, to enhance its therapeutic effects.
The comprehensive research on UDCA reflects its importance in the treatment of liver and digestive system disorders. However, the specific use of UDCA and its dosage should be determined by a healthcare professional based on individual patient needs and conditions. Researchers continue to explore its potential applications and underlying mechanisms, which may lead to further therapeutic innovations.
