Vitamin K2, also known as menaquinone, is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in various biological processes, primarily related to blood clotting and bone health. Comprehensive research on Vitamin K2 has uncovered its functions, sources, benefits, and potential health implications. Here’s an overview of what is known about Vitamin K2:
1.Types of Vitamin K:
Vitamin K exists in two primary forms: Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) and Vitamin K2 (menaquinone). Vitamin K1 is primarily involved in blood clotting, while Vitamin K2 has additional roles in bone health and other physiological processes.
2.Sources of Vitamin K2:
Vitamin K2 is found in various food sources, with the highest amounts typically found in fermented foods. Common sources include natto (fermented soybeans), cheese (particularly hard and soft cheeses), egg yolks, meat, and poultry. It can also be synthesized by certain gut bacteria.

3.Functions and Benefits of Vitamin K2:
Blood Clotting: Like Vitamin K1, Vitamin K2 plays a critical role in blood clotting by facilitating the activation of clotting factors in the liver.
Bone Health: Vitamin K2 helps regulate calcium metabolism in the body. It activates proteins that direct calcium to the bones, preventing its accumulation in soft tissues and arteries. This is important for maintaining bone density and preventing conditions like osteoporosis.
Cardiovascular Health: Some research suggests that adequate Vitamin K2 intake may reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases by preventing arterial calcification.
Dental Health: Vitamin K2 may contribute to dental health by supporting proper calcium metabolism in teeth and preventing tooth decay.
Cancer Prevention: Some studies have indicated a potential role for Vitamin K2 in reducing the risk of certain types of cancer, such as prostate cancer.
4.Recommended Dietary Intake:
The recommended dietary intake for Vitamin K2 has not been established as thoroughly as for Vitamin K1. However, it is generally recommended to include foods rich in Vitamin K2 in your diet to ensure adequate intake. The optimal dosage can vary depending on individual health needs and factors.
5.Absorption and Metabolism:
Vitamin K2 is fat-soluble, and its absorption is enhanced when consumed with dietary fats. The liver is responsible for storing and activating Vitamin K2, and it is transported in the bloodstream to target tissues.
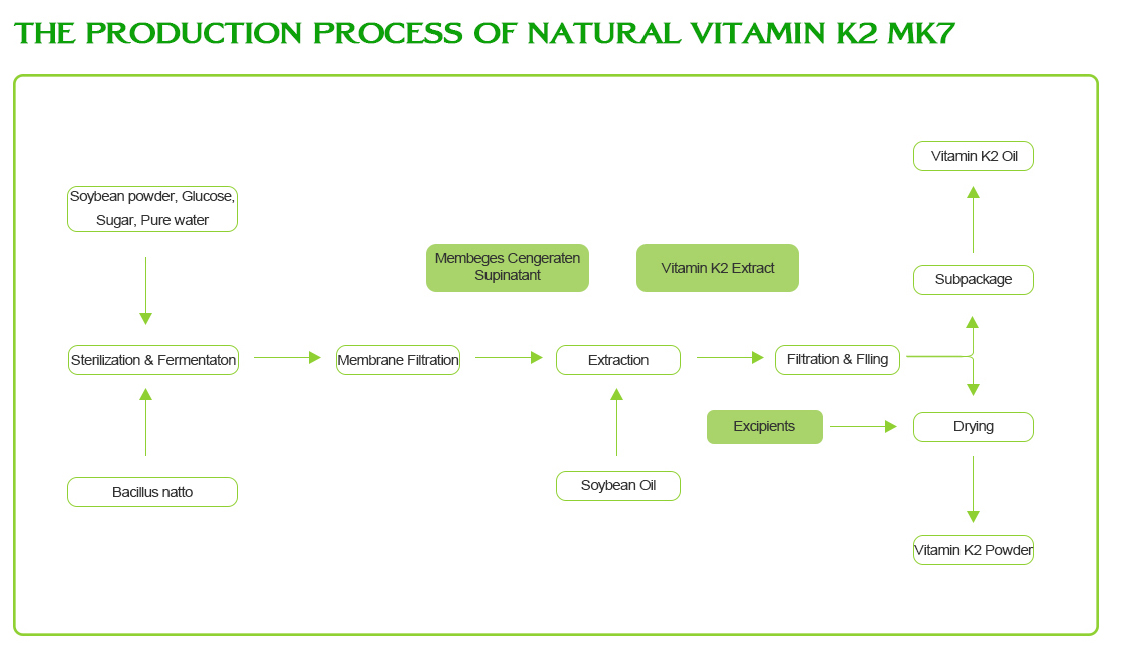
6.Deficiency and Health Implications:
Vitamin K2 deficiency is relatively rare, but it can lead to increased bleeding tendencies, reduced bone mineralization, and an increased risk of cardiovascular and other health issues.
Some individuals at a higher risk of deficiency include those with certain medical conditions, malabsorption issues, or a limited intake of Vitamin K2-rich foods.
7.Safety:
Vitamin K2 is generally considered safe when consumed in reasonable amounts through a balanced diet. There are no established tolerable upper intake levels for Vitamin K2, but excessive intake from supplements may lead to adverse effects, including interference with blood-thinning medications.
Comprehensive research on Vitamin K2 is ongoing, and it continues to shed light on its importance in various aspects of health. It is advisable to maintain a balanced diet that includes Vitamin K2-rich foods to support overall health and well-being. If you have specific health concerns or dietary questions related to Vitamin K2, it’s best to consult a healthcare professional or nutritionist for personalized guidance.
