Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is an ancient medicinal herb commonly used in Ayurvedic medicine. Its roots and leaves are used to produce Ashwagandha extract, which is known for its potential health benefits, including reducing stress, improving cognitive function, and enhancing overall well-being. The extraction process involves several steps to obtain the active compounds from the plant material. Here’s an overview of the typical extraction process:
Harvesting: Ashwagandha plants are typically harvested when they reach maturity, which is usually after about four to five months of growth. The roots and leaves are the primary parts used for extraction.
Drying: After harvesting, the plant material is cleaned to remove dirt and other impurities. The roots and leaves are then dried to reduce their moisture content, which helps prevent spoilage during storage and extraction.
Grinding: The dried roots and leaves are finely ground into a coarse powder. This increases the surface area of the plant material, making it easier for the active compounds to be extracted.
Solvent extraction: The ground Ashwagandha powder is then subjected to a solvent extraction process. Commonly used solvents include water, alcohol (ethanol), or a combination of both (hydroalcoholic extraction). Ethanol is often preferred as it can effectively extract both water-soluble and alcohol-soluble compounds.
Filtering: After the extraction process, the mixture of solvent and extracted compounds is filtered to remove any remaining solid particles, leaving a crude Ashwagandha extract.

Concentration: The crude extract may undergo further processing to concentrate the active compounds. This can be achieved through various methods, such as vacuum evaporation or spray drying, which removes the solvent and leaves behind a more concentrated extract.
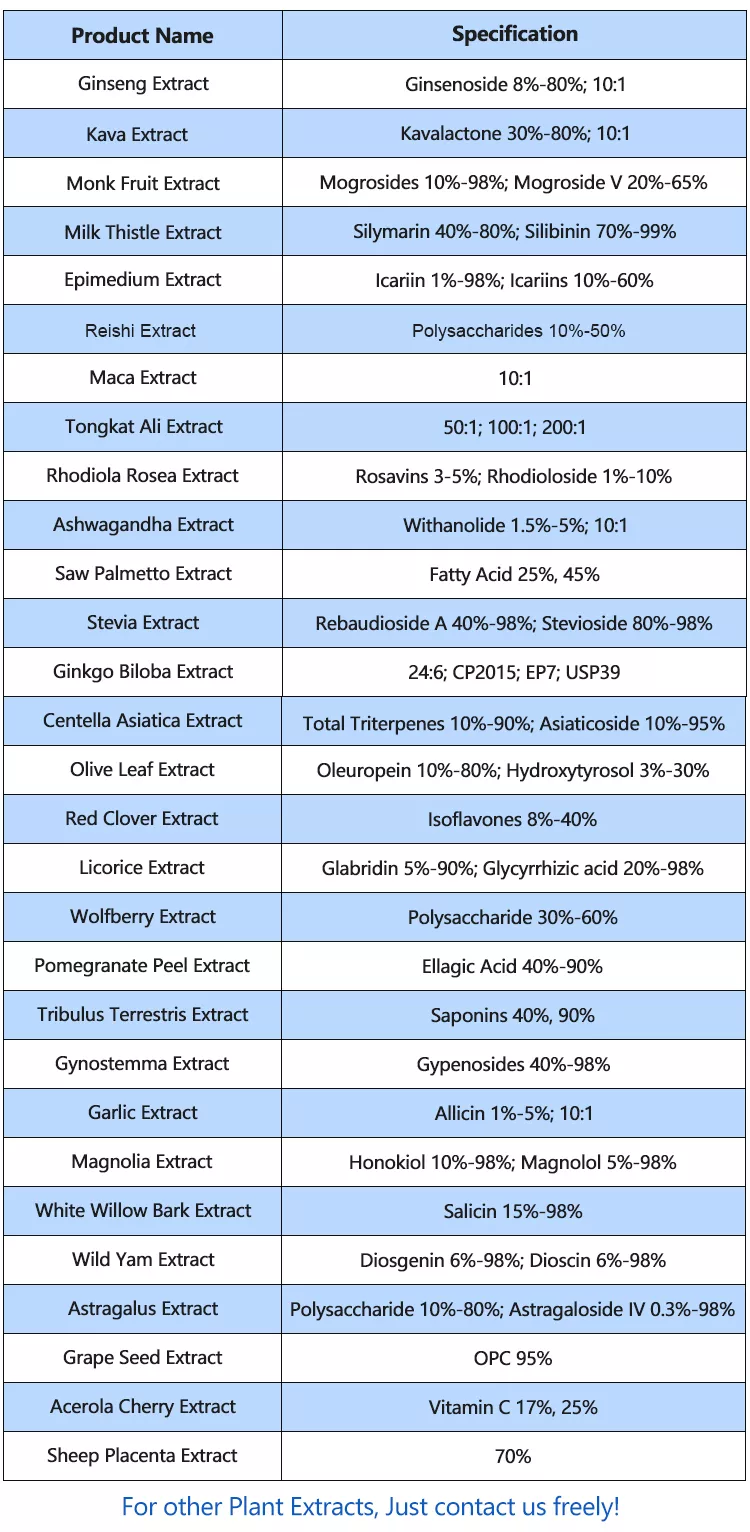
Standardization: To ensure consistency and potency, the extract may be standardized to a specific concentration of key active compounds, such as withanolides, which are believed to be responsible for many of Ashwagandha’s health benefits.
Quality control and testing: Throughout the extraction process, quality control measures are taken to ensure the extract meets safety and efficacy standards. This may include testing for the presence of contaminants and verifying the concentration of active compounds.
Packaging and storage: The final Ashwagandha extract is then packaged in suitable containers and stored in a cool, dry place to maintain its stability and potency.
It’s important to note that the extraction process may vary depending on the manufacturer and the intended use of the Ashwagandha extract. Additionally, while Ashwagandha is generally considered safe for most people when used as directed, it’s always best to consult with a healthcare professional before using any herbal supplement, especially if you have existing health conditions or are taking medications.
