Minoxidil is a medication that is primarily used to treat hair loss, specifically androgenetic alopecia, which is commonly referred to as male or female pattern baldness. It was originally developed for a different purpose and its hair growth effects were discovered incidentally. Here’s some information on the origin and nature of minoxidil:
Origin of Minoxidil:
Minoxidil was initially developed in the late 1950s by the Upjohn Company, which is now a part of Pfizer. The original intent behind its development was to create a medication for the treatment of high blood pressure, specifically severe hypertension. It was initially marketed as an oral medication under brand names like Loniten for this purpose.

Discovery of Hair Growth Effects:
During clinical trials for minoxidil as an oral hypertension medication, researchers observed an unexpected side effect: increased hair growth in some participants. This serendipitous discovery led to further research on minoxidil’s potential for promoting hair growth. As a result, in 1988, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the topical use of minoxidil as a treatment for male pattern baldness. Subsequently, it was also approved for female pattern baldness.
Nature of Minoxidil:
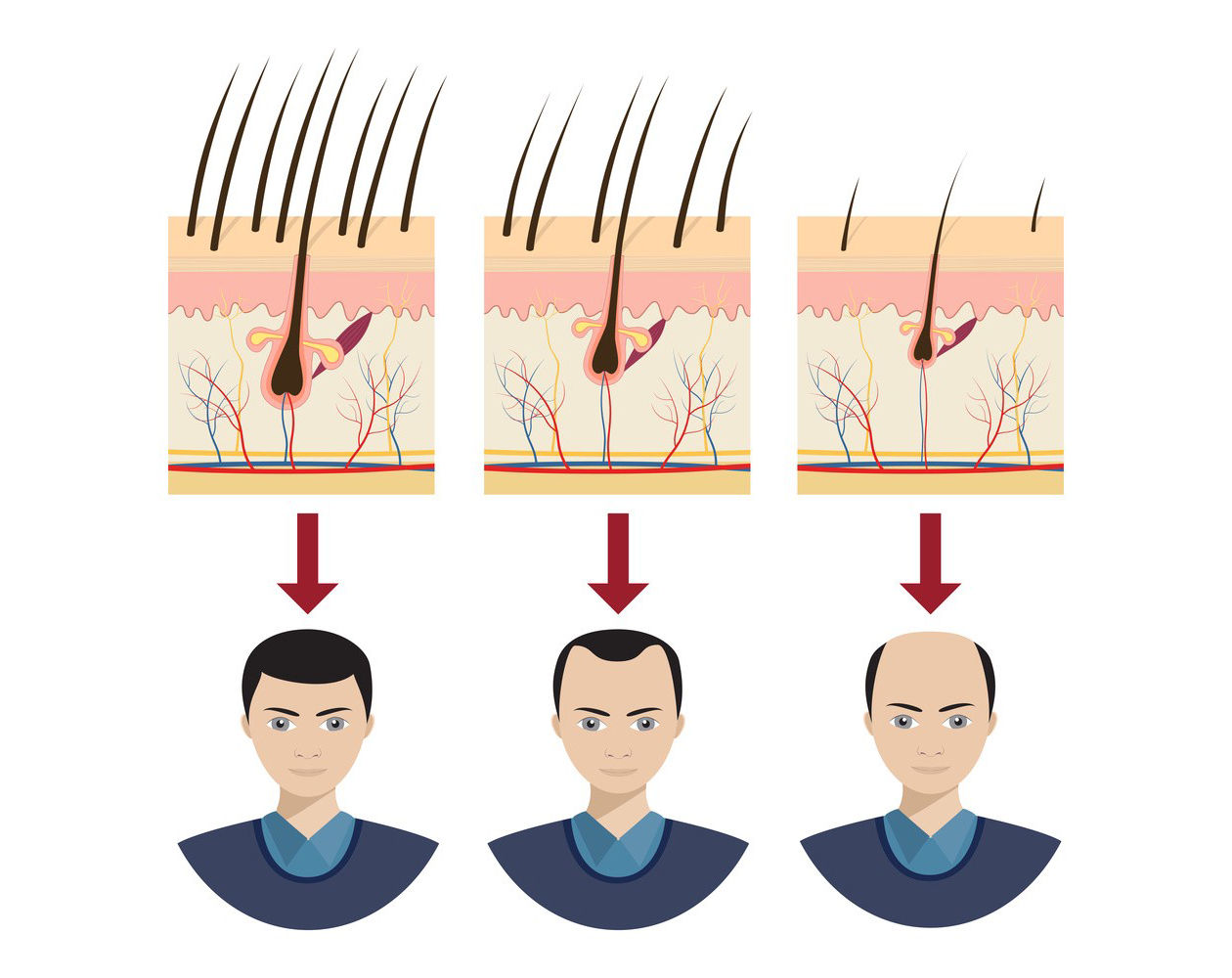
Minoxidil is a vasodilator, which means it relaxes blood vessels and allows for increased blood flow. In the context of hair loss treatment, its exact mechanism of action is not fully understood, but it is believed to work in several ways:
- Dilation of Blood Vessels: Minoxidil applied topically increases blood flow to the hair follicles, which may provide more nutrients and oxygen to the hair follicles, promoting hair growth.
- Prolonging Anagen Phase: Minoxidil may prolong the anagen (growth) phase of hair follicles, resulting in thicker and longer hair strands.
- Potassium Channel Opening: It is thought to open potassium channels in cells, which can lead to increased hair follicle cell activity.
Minoxidil is available in various forms, including topical solutions and foams, which are applied directly to the scalp. It is typically used as a long-term treatment and requires consistent application to maintain results. It is worth noting that the exact efficacy of minoxidil can vary from person to person, and not everyone responds to it equally.
In summary, minoxidil was originally developed as an oral medication for hypertension but was later found to have the side effect of promoting hair growth when applied topically. It is now widely used to treat male and female pattern baldness, although its exact mechanism of action in promoting hair growth is not fully understood.
Potential Benefits of Minoxidil
Minoxidil is a medication that is primarily used to treat hair loss, particularly male pattern baldness (androgenetic alopecia) and female pattern baldness. While its exact mechanism of action isn’t fully understood, it is believed to promote hair growth by:
1.Vasodilation: Minoxidil is a vasodilator, meaning it widens the blood vessels. This can increase blood flow to the hair follicles, delivering more nutrients and oxygen, which may promote hair growth.
2.Prolonging the Anagen Phase: Minoxidil may prolong the anagen (growth) phase of the hair follicle’s growth cycle, allowing hairs to grow longer and thicker.
Here are some potential benefits of minoxidil:
1.Hair Regrowth: Minoxidil has been proven effective in many clinical studies in promoting hair regrowth in individuals with androgenetic alopecia, both in men and women.
2.Prevention of Further Hair Loss: It can help prevent further hair loss by stabilizing hair follicles that are susceptible to miniaturization due to the effects of dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
3.Improved Hair Thickness: Minoxidil can increase the thickness of existing hair strands, giving the appearance of fuller hair.
4.Easy Application: It is available in various forms, including topical solutions and foams, making it easy to apply.
5.Over-the-Counter Availability: In many countries, minoxidil is available without a prescription, making it accessible to a wide range of individuals seeking hair loss treatment.
6.Minimal Side Effects: Minoxidil generally has few systemic side effects, although some individuals may experience scalp irritation, itching, or dryness. These side effects are usually mild and can often be managed.
7.Compatibility with Other Treatments: Minoxidil can be used in combination with other hair loss treatments, such as finasteride, to potentially enhance results.
It’s important to note that the effectiveness of minoxidil can vary from person to person, and not everyone will experience significant hair regrowth. Additionally, the benefits typically diminish if the medication is discontinued, and long-term use may be necessary to maintain results.
Before starting minoxidil or any other medication for hair loss, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist to determine the most suitable treatment for your specific condition and to discuss any potential side effects or concerns.
