Vitamin K2, also known as menaquinone, is a fat-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in several physiological processes in the human body, primarily related to blood clotting and bone metabolism. There are several forms of vitamin K2, with menaquinone-4 (MK-4) and menaquinone-7 (MK-7) being the most well-studied.
Origin of Vitamin k2:
Vitamin K2 is not typically found in significant amounts in the human diet; rather, it is synthesized by bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract. It is also found in certain animal-based foods, particularly in fermented foods and organ meats. The primary dietary sources of vitamin K2 include:
1.Fermented Foods: Natto, a Japanese dish made from fermented soybeans, is one of the richest dietary sources of vitamin K2 (MK-7).
2.Fermented Dairy: Certain cheeses, like Gouda and Brie, are also good sources of vitamin K2.
3.Organ Meats: Liver and other organ meats contain vitamin K2.
4.Animal Fat: Fats from animals that have consumed grass or other vitamin K-rich foods may also contain vitamin K2.
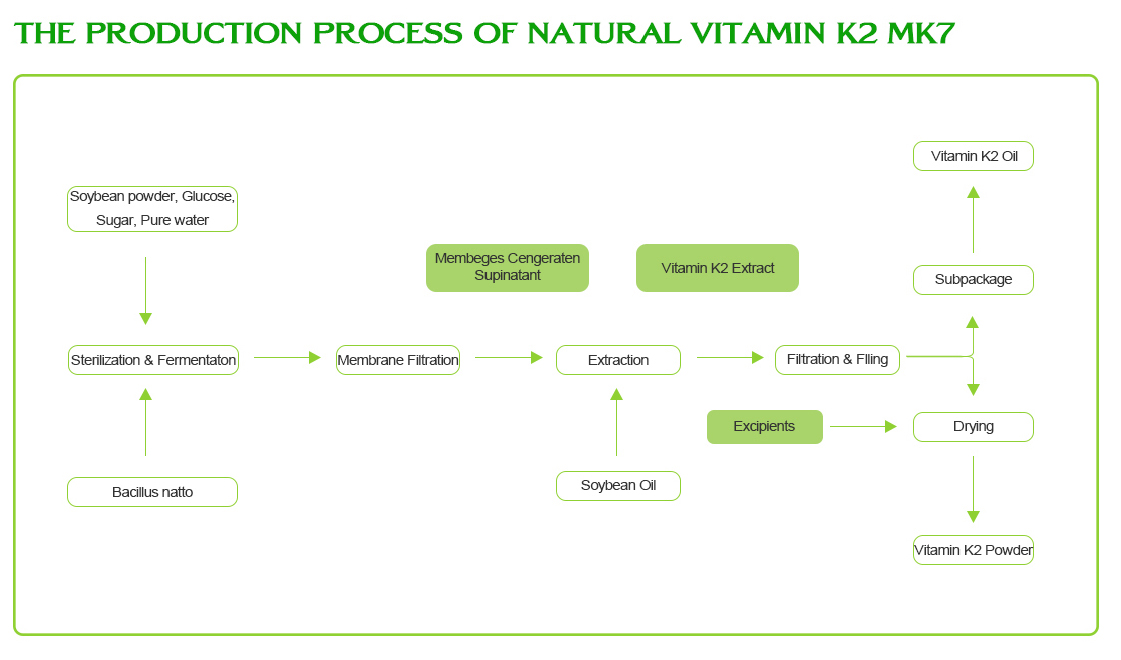
Nature of Vitamin k2:
Vitamin K2 is a family of compounds, with different menaquinones (MKs) being classified based on the length of their side chains. The two primary forms of vitamin K2 are MK-4 and MK-7, which differ in the length of their side chains. The nature of vitamin K2 is as follows:
1.Menaquinone-4 (MK-4): MK-4 is a shorter-chain menaquinone found in some animal products and produced by the conversion of vitamin K1 (phylloquinone) in the body. It has a relatively short half-life and is not as well-distributed throughout the body compared to MK-7.
2.Menaquinone-7 (MK-7): MK-7 is a longer-chain menaquinone that is more bioavailable and has a longer half-life in the body. It is produced by certain bacteria and can be found in fermented foods like natto. MK-7 is considered more effective at maintaining healthy bones and preventing arterial calcification because of its longer half-life.
Vitamin K2 is essential for activating specific proteins in the body, such as osteocalcin (involved in bone health) and matrix Gla protein (involved in cardiovascular health). These proteins require vitamin K2-dependent modifications to function properly.
In summary, vitamin K2 is a fat-soluble vitamin that is primarily synthesized by bacteria in the gut and found in certain dietary sources. It plays a crucial role in bone health and cardiovascular health by supporting the activation of specific proteins in the body, and its various forms, particularly MK-4 and MK-7, have different characteristics and functions.
Potential Benefits of Vitamin k2
Vitamin K2, also known as menaquinone, is a lesser-known but essential fat-soluble vitamin that plays several important roles in the body. While it shares some functions with Vitamin K1 (phylloquinone), it is particularly involved in regulating calcium metabolism and bone health. Here are some potential benefits of Vitamin K2:
Bone Health: Vitamin K2 activates a protein called osteocalcin, which helps incorporate calcium into the bone matrix. This mineralization process is crucial for maintaining bone density and preventing osteoporosis. Adequate Vitamin K2 intake can reduce the risk of fractures and improve bone strength.
Cardiovascular Health: Vitamin K2 helps prevent the buildup of calcium in arterial walls and soft tissues. This can reduce the risk of atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries) and decrease the likelihood of cardiovascular events like heart attacks and strokes.

Dental Health: Proper calcium metabolism is essential for maintaining healthy teeth. Vitamin K2 may contribute to dental health by supporting the mineralization of tooth enamel and dentin.
Cancer Prevention: Some studies suggest that Vitamin K2 may have a role in cancer prevention, particularly in reducing the risk of certain types of cancer, including prostate, liver, and lung cancer. The exact mechanisms are still under investigation.
Improved Insulin Sensitivity: Emerging research has indicated that Vitamin K2 may have a positive impact on insulin sensitivity, which can help in managing blood sugar levels and reducing the risk of type 2 diabetes.
Anti-Inflammatory Effects: Vitamin K2 may have anti-inflammatory properties and can help modulate the immune response in the body.
Skin Health: Some studies suggest that Vitamin K2 can support skin health by helping with wound healing and reducing the appearance of skin conditions such as stretch marks and varicose veins.
It’s important to note that the recommended dietary allowances for Vitamin K2 have not been firmly established, and the optimal intake may vary among individuals. Vitamin K2 is naturally found in foods such as fermented dairy products (e.g., cheese, yogurt), organ meats, and certain fermented foods (e.g., natto). It is also available in supplement form.
As with any nutrient, it’s essential to maintain a balanced diet and consult with a healthcare professional before taking supplements, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications. Overdosing on fat-soluble vitamins like Vitamin K2 can have adverse effects, so it’s important to use supplements cautiously and under professional guidance.
