Proteases, also known as peptidases or proteolytic enzymes, are a class of enzymes that play a crucial role in breaking down proteins into smaller peptides and amino acids. They have various applications and come with their own set of pros and cons. Here are some of the key advantages and disadvantages of proteases:
Pros of Proteases:
Digestive Aid: In the human body, proteases are essential for the digestion of dietary proteins. They help break down proteins in the stomach and small intestine, facilitating their absorption as amino acids, which are necessary for various bodily functions.
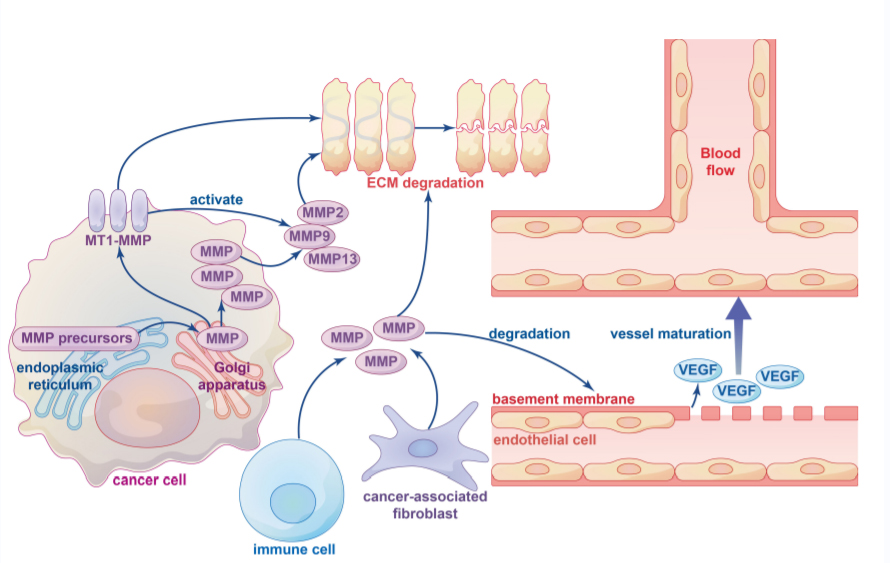
Biological Functions: Proteases are involved in numerous essential biological processes, such as blood clotting, cell signaling, and the regulation of cell cycle and apoptosis.
Industrial and Biotechnological Applications: Proteases find use in various industrial and biotechnological processes. They are employed in the food industry to tenderize meat, in the production of cheese and other dairy products, and in the manufacture of detergents and cleaning products to break down protein-based stains.
Research Tools: Proteases are valuable tools in molecular biology and biochemistry research. They are used to cleave proteins at specific sites, facilitating the study of protein structure and function.
Therapeutic Potential: Proteases are explored as potential therapeutic agents in various medical fields. They can be used to treat conditions where excess protein accumulation is problematic, such as in some neurodegenerative diseases.
Cons of Proteases:
Potential for Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may be sensitive or allergic to certain proteases, leading to adverse reactions when exposed to products or medications containing these enzymes.
Tissue Damage: In certain medical conditions, proteases can cause tissue damage if their activity is not properly regulated. For example, in diseases like pancreatitis, the pancreas’s digestive enzymes, including proteases, can damage pancreatic tissue.
Inhibition of Other Enzymes: Proteases can interfere with the activity of other enzymes, particularly those involved in coagulation. This can be problematic in some medical situations.

Environmental Impact: In some industrial applications, the release of protease-containing wastewater can have environmental consequences if not properly treated.
Regulation and Safety Concerns: The use of proteases in food production and other industries is subject to regulatory oversight to ensure safety and proper labeling. Contamination or mislabeling can pose risks to consumers.
Specificity: Proteases can have varying levels of specificity, meaning they may not always cleave proteins at the desired sites. This can be a limitation in some research and biotechnological applications.
In summary, proteases have significant benefits in digestion, various industrial processes, and research, but they also come with potential drawbacks related to allergies, tissue damage, and regulatory concerns. As with any enzyme or substance, their use should be carefully considered in different applications to maximize their advantages while minimizing potential risks.
