Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is a medication primarily used to treat certain liver diseases and conditions. It is a bile acid that can help improve liver function and reduce the symptoms associated with certain liver disorders. Here are some of the pros and cons of UDCA:
Pros of UDCA:
Treatment of Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC): UDCA is the first-line treatment for primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), a chronic autoimmune liver disease. It can slow down the progression of the disease and improve liver function.
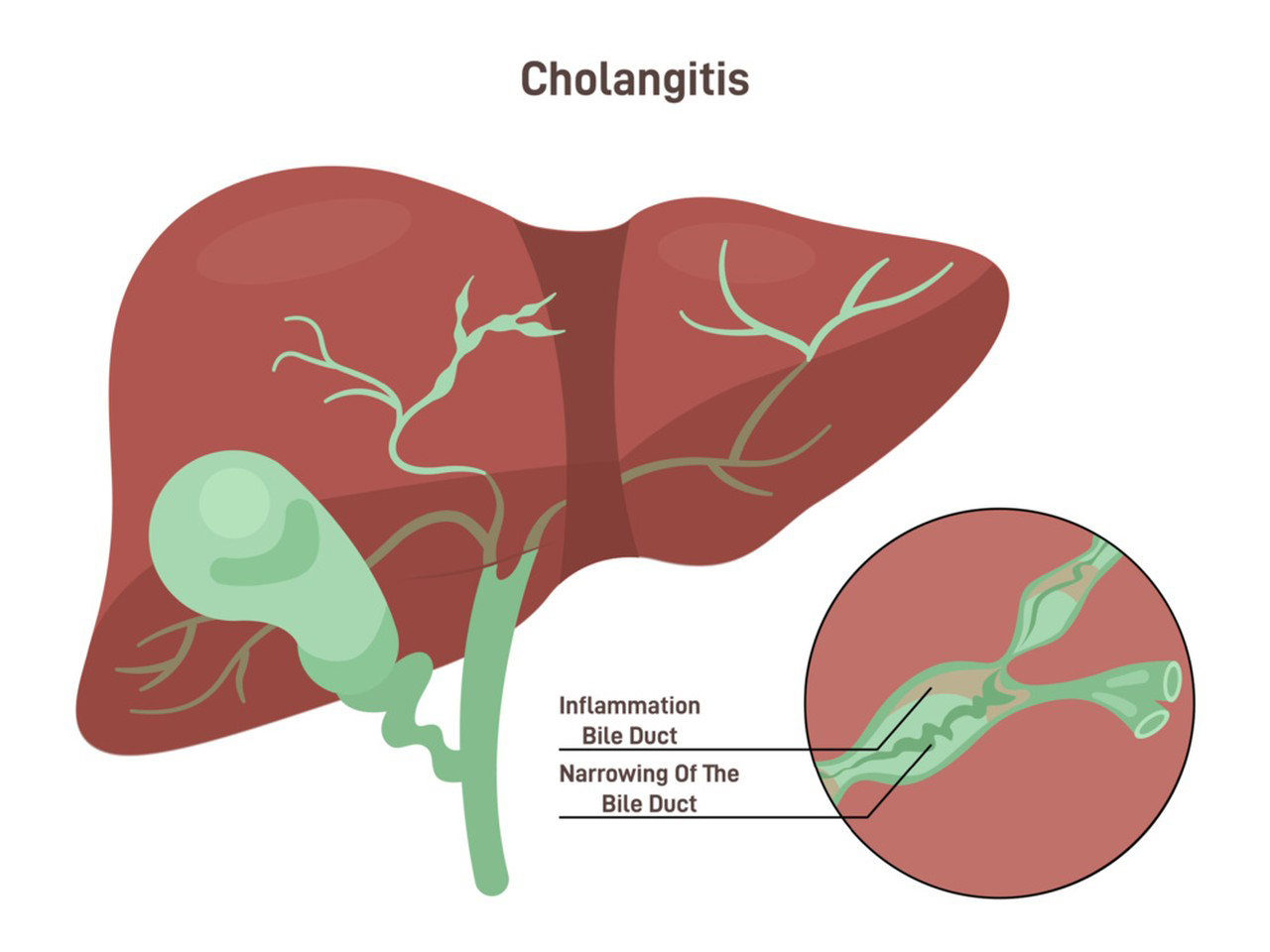
Treatment of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC): UDCA is sometimes used to manage primary sclerosing cholangitis, another chronic liver disease. While its efficacy in PSC is still a matter of debate, it is sometimes prescribed to relieve symptoms and slow disease progression.
Dissolution of Gallstones: UDCA can be used to dissolve small cholesterol gallstones, although it is not the first-line treatment for gallstones. It may be considered for individuals who are not candidates for surgery.
Well-Tolerated: UDCA is generally well-tolerated, and serious side effects are rare. It has a good safety profile when used as directed by a healthcare provider.
Cons of UDCA:
Limited Efficacy: UDCA may not be effective in all patients with liver diseases. Its effectiveness varies depending on the specific condition and the individual. In some cases, it may not prevent disease progression or improve liver function significantly.
Cost: UDCA can be expensive, particularly for those without insurance coverage. The cost may be a significant drawback for some individuals.
Gallstone Recurrence: If UDCA is used to dissolve gallstones, there is a risk of gallstone recurrence once the treatment is discontinued. It may not provide a permanent solution to gallstone problems.
Side Effects: While UDCA is generally well-tolerated, it can cause side effects in some people. These can include diarrhea, abdominal pain, and elevated liver enzyme levels. Rarely, severe adverse effects such as liver toxicity can occur.

Drug Interactions: UDCA can interact with other medications, potentially reducing their effectiveness. It’s important for healthcare providers to be aware of all the medications a patient is taking to avoid potential drug interactions.
Not a Cure: UDCA is not a cure for liver diseases. It can slow down disease progression, alleviate symptoms, or dissolve gallstones, but it does not eliminate the underlying causes of these conditions.
The decision to use UDCA should be made by a healthcare provider based on the specific diagnosis and needs of the patient. It is essential to weigh the potential benefits and risks in each individual case and consider other treatment options when necessary. Patients should consult with their healthcare provider for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
