Urolithin A is a metabolite produced by the gut microbiota from ellagic acid, which is found in various fruits and nuts, particularly in pomegranates and certain berries. While research on Urolithin A is still in its early stages, there are some potential benefits and drawbacks associated with its consumption.
Pros of Urolithin A:
Anti-inflammatory Properties: Urolithin A has been studied for its potential anti-inflammatory effects, which may contribute to reducing inflammation in the body.
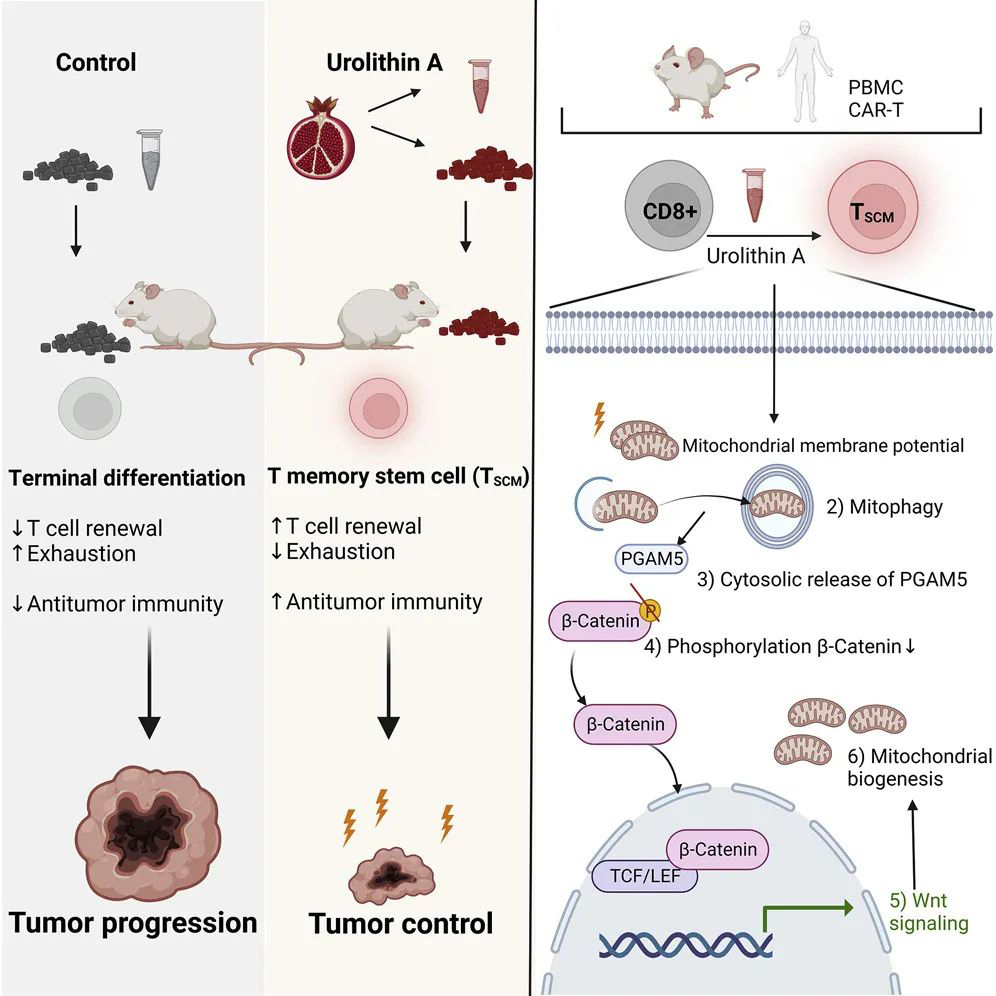
Mitochondrial Health: Some research suggests that Urolithin A may support mitochondrial health and function. Mitochondria are the energy-producing organelles in cells, and maintaining their health is crucial for overall cellular function.

Muscle Health and Exercise Performance: Preliminary studies indicate that Urolithin A might have a positive impact on muscle health and exercise performance by promoting muscle cell renewal and enhancing the efficiency of energy production.
Potential Anti-Aging Effects: Urolithin A has been investigated for its potential anti-aging properties, particularly in relation to cellular and mitochondrial health.
Neuroprotective Effects: Some studies suggest that Urolithin A may have neuroprotective effects, potentially benefiting brain health and reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
Cons of Urolithin A:
Limited Human Studies: Much of the research on Urolithin A is still in the early stages, and there is a limited amount of human clinical data available. Therefore, more research is needed to fully understand its effects on humans.
Individual Variability: The production of Urolithin A in the body depends on the gut microbiota, and individuals may vary in their ability to produce this metabolite. Factors such as diet, gut health, and genetics can influence the production of Urolithin A.
Unknown Long-Term Effects: Since research on Urolithin A is relatively recent, the long-term effects of its regular consumption are not well-established. It’s important to exercise caution until more comprehensive studies are conducted.
Potential Side Effects: While Urolithin A appears to be generally well-tolerated, some individuals may experience side effects. These could include gastrointestinal discomfort or allergic reactions. However, such occurrences seem to be rare.
Limited Food Sources: Urolithin A is derived from ellagic acid found in specific foods like pomegranates and certain berries. If individuals do not regularly consume these foods, they may not experience the potential benefits associated with Urolithin A.
It’s crucial to note that the field of research on Urolithin A is evolving, and more studies are needed to confirm its potential benefits and drawbacks. Individuals considering Urolithin A supplementation should consult with healthcare professionals to ensure safety and appropriateness based on individual health conditions and goals.
