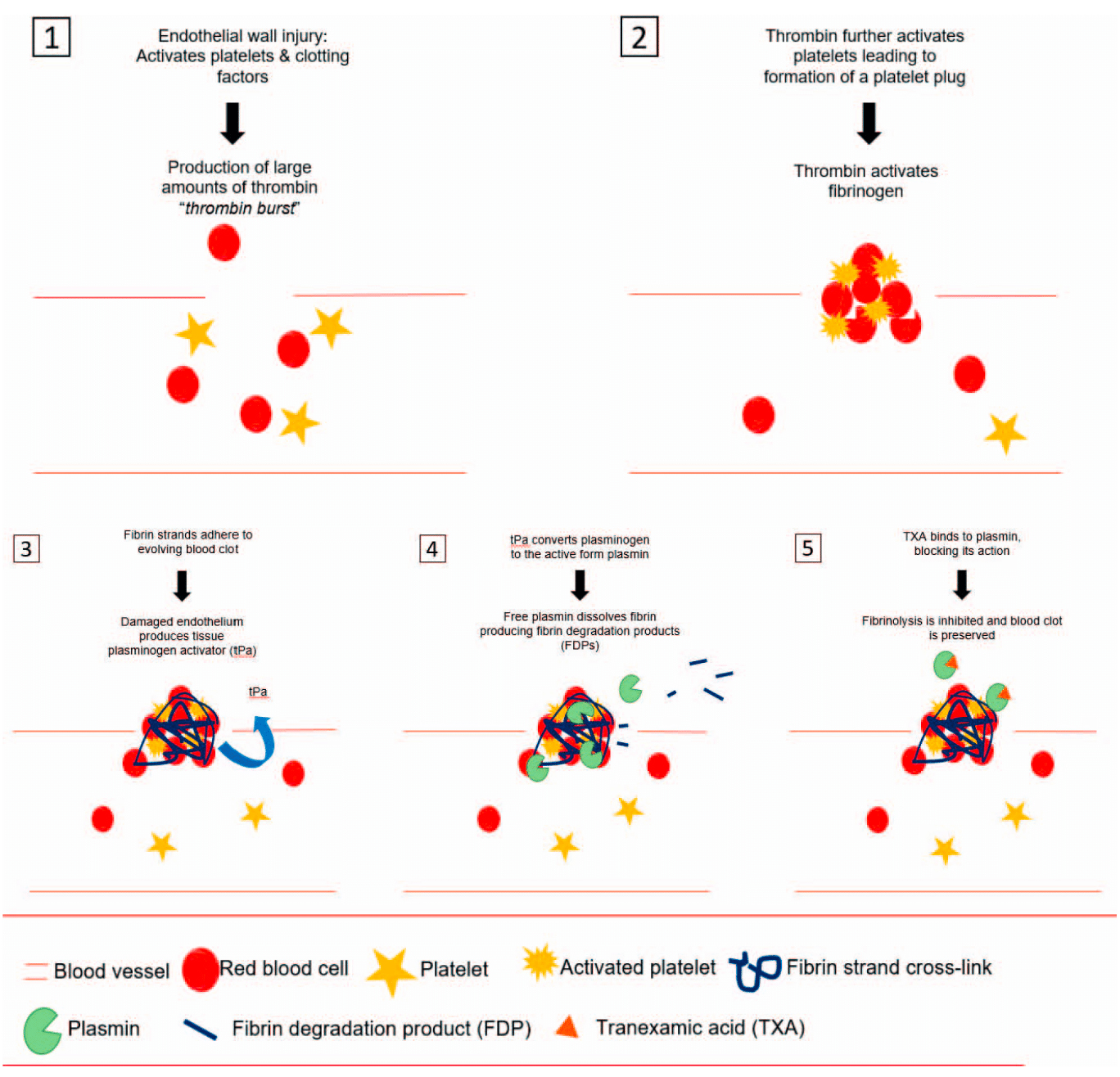
Tranexamic acid is commonly used to treat or prevent excessive bleeding, as it helps to reduce blood loss by inhibiting fibrinolysis, the process that breaks down blood clots. It’s a synthetic antifibrinolytic agent, meaning it helps stabilize blood clots and can be used in various medical situations.
Here are the main uses and treatments for tranexamic acid:
1. Menorrhagia (Heavy Menstrual Bleeding)
- Dosage: Usually 1 gram taken 2-3 times daily for up to 5 days during menstruation.
- Mechanism: It reduces the amount of menstrual bleeding by preventing the breakdown of clots.
2. Trauma or Surgery-Related Bleeding
- Dosage: In surgery or trauma, it can be administered intravenously (IV). A typical IV dose might be 1 gram over 10 minutes, followed by additional doses depending on the clinical situation.
- Mechanism: Tranexamic acid is used to minimize blood loss during surgeries like orthopedic procedures, cardiac surgeries, or during trauma to help reduce the risk of hemorrhage.

3. Postpartum Hemorrhage (PPH)
- Dosage: Intravenous infusion during childbirth or immediately following delivery to help control bleeding.
- Mechanism: It helps reduce postpartum bleeding by stabilizing blood clots that may have been disrupted after delivery.
4. Nosebleeds (Epistaxis)
- Dosage: Topical use in the form of nasal sprays or direct application to the bleeding site can be effective.
- Mechanism: It helps stop the breakdown of clots in the nasal mucosa, thus controlling bleeding.
5. Dental Procedures
- Dosage: Sometimes prescribed to patients undergoing dental procedures (especially those with bleeding disorders or after oral surgery).
- Mechanism: Prevents excessive bleeding by stabilizing the clots that form in the mouth.
6. Other Conditions
- It is also sometimes used for bleeding in conditions like hemophilia, and certain cancers, or as a preventive measure for bleeding in high-risk surgeries.
Side Effects of Tranexamic Acid
- Common side effects include gastrointestinal upset (like nausea, vomiting), headache, or dizziness.
- Rare but serious side effects include blood clots (thrombosis), so caution is needed in patients with a history of clotting disorders or those at high risk for clotting.
Contraindications
- Should not be used in people with active thromboembolic disorders (e.g., deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism).
- Caution in patients with renal impairment, as it can accumulate in the kidneys.
Would you like more detailed information about a specific use of tranexamic acid or its mechanisms?
