UDCA (Ursodeoxycholic Acid) is a bile acid used for various medical conditions related to the liver and gallbladder.
Uses of UDCA
1. Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC)
UDCA is the first-line treatment for primary biliary cholangitis, a chronic liver disease that causes bile duct damage and leads to cirrhosis. It helps slow disease progression and improves liver function.
2. Gallstone Dissolution
Used to dissolve small cholesterol gallstones in patients who cannot undergo surgery. It works by reducing cholesterol secretion and increasing bile flow.
3. Cystic Fibrosis-Related Liver Disease
Helps improve bile flow and reduce liver damage in patients with cystic fibrosis who develop liver complications.
4. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) & Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
UDCA has been studied for its potential to improve liver enzymes and reduce liver inflammation in NAFLD and NASH, although its benefits remain controversial.
5. Intrahepatic Cholestasis of Pregnancy (ICP)
Helps relieve itching (pruritus) and improves liver function in pregnant women with cholestasis, a condition where bile flow is impaired.
6. Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis (PSC)
Sometimes used as an adjunct treatment to improve liver enzymes and bile flow in primary sclerosing cholangitis, though its effectiveness is debated.
7. Liver Protection in Certain Conditions
Used to protect the liver in drug-induced liver injury and after liver transplantation to prevent bile flow-related complications.
Would you like more details on any of these uses?
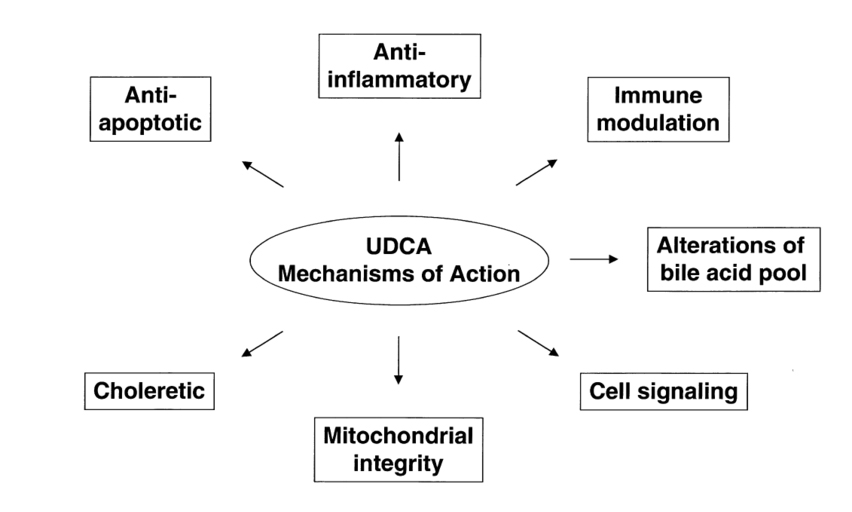
Pharmacological action of UDCA
UDCA (Ursodeoxycholic Acid) exerts its pharmacological effects primarily in the liver and gastrointestinal tract. Its key actions include:
- Hepatoprotective Action – UDCA stabilizes hepatocyte membranes, protects liver cells from bile acid-induced toxicity, and reduces oxidative stress.
- Choleretic Effect – UDCA enhances bile flow (choleresis) by reducing bile acid toxicity, increasing bile acid secretion, and decreasing bile saturation with cholesterol.
- Cytoprotective Effect – It reduces apoptosis and oxidative stress in hepatocytes, protecting liver cells from damage.

- Immunomodulatory Effect – UDCA modulates the immune response by decreasing the expression of major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class I and II molecules, reducing pro-inflammatory cytokine production.
- Anti-lithogenic Effect – UDCA reduces cholesterol saturation in bile, inhibiting cholesterol crystallization and promoting the dissolution of cholesterol gallstones.
- Anti-fibrotic Action – UDCA may slow the progression of liver fibrosis by reducing bile acid-induced hepatocyte injury and inflammation.
These actions make UDCA useful in treating primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), gallstone disease, and other cholestatic liver disorders.
