Vitamin U is not technically a vitamin but rather a term used to describe a compound called S-methylmethionine (SMM). It was first discovered in the 1950s and is known for its potential health benefits, particularly in relation to the digestive system.
Uses of Vitamin U
1. Gut Health and Ulcers:
- Vitamin U has been studied for its ability to help heal ulcers, especially peptic ulcers. It is thought to promote the healing of the stomach lining and reduce inflammation.
- Some studies suggest that it can help protect the digestive tract from irritation caused by things like alcohol or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
2. Anti-inflammatory Properties:
- Due to its potential to reduce inflammation, Vitamin U might be helpful for people with inflammatory conditions of the digestive tract, like gastritis.

3. Promoting Healthy Digestion:
- It may support the overall function of the digestive system by promoting healthy mucous production, which can help protect the stomach and intestines from damage.
4. Supporting Liver Health:
- There is some evidence suggesting that Vitamin U may have a positive effect on liver health, potentially promoting detoxification and reducing liver inflammation.
5. Wound Healing:
- Some proponents of Vitamin U claim that it can aid in the healing of wounds, especially those related to the digestive tract, by supporting cell regeneration.
Sources:
- Vitamin U is typically found in raw cabbage juice, which was one of the first foods identified as a source of the compound.
- Other foods that contain small amounts of Vitamin U include leafy green vegetables, legumes, and whole grains.
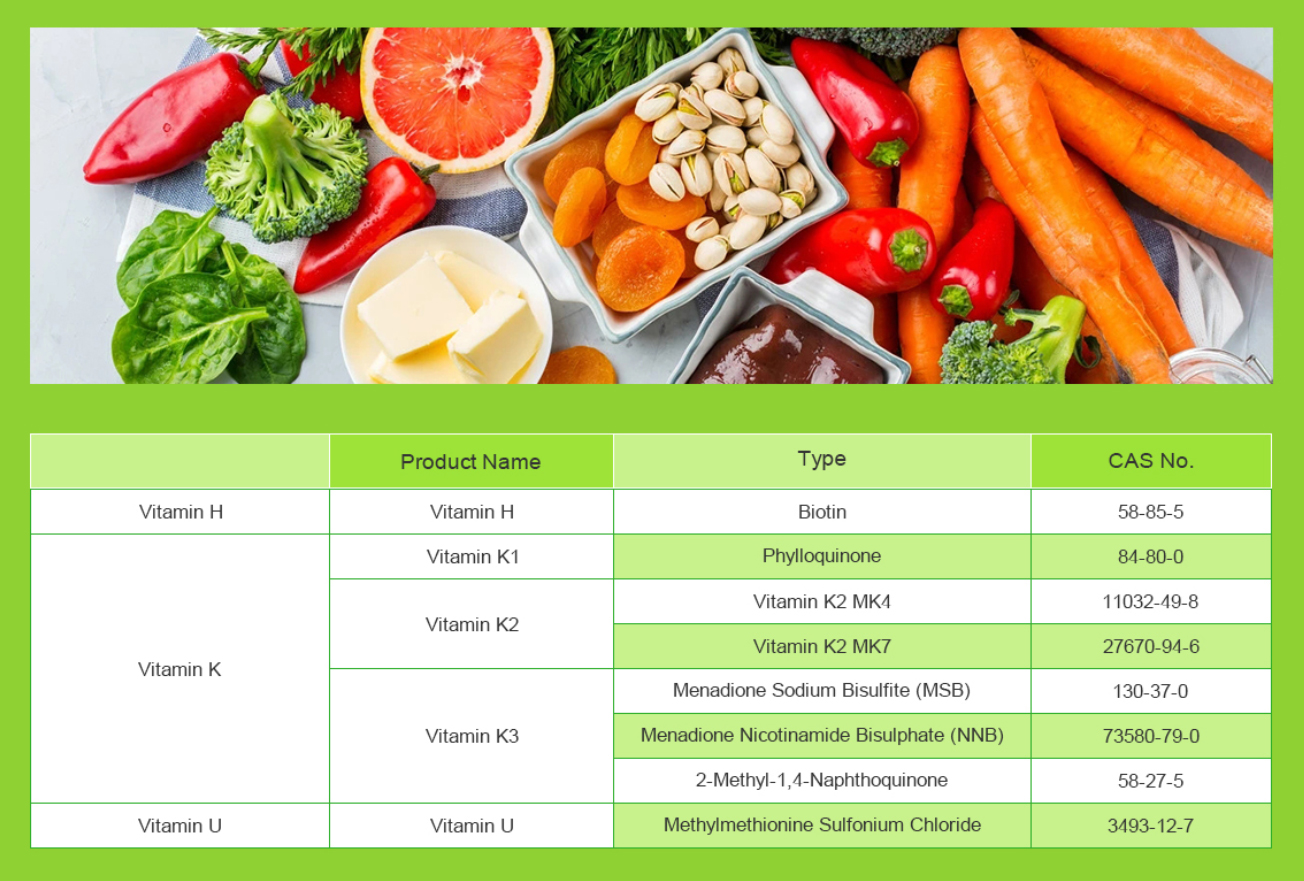
Though Vitamin U is not a formally recognized nutrient like Vitamin A or C, its potential benefits, particularly in relation to gut health, have made it an area of interest for some natural health proponents. However, more research is needed to fully understand its effects.
Would you like to explore any of these uses further or talk about how to incorporate it into your diet?
