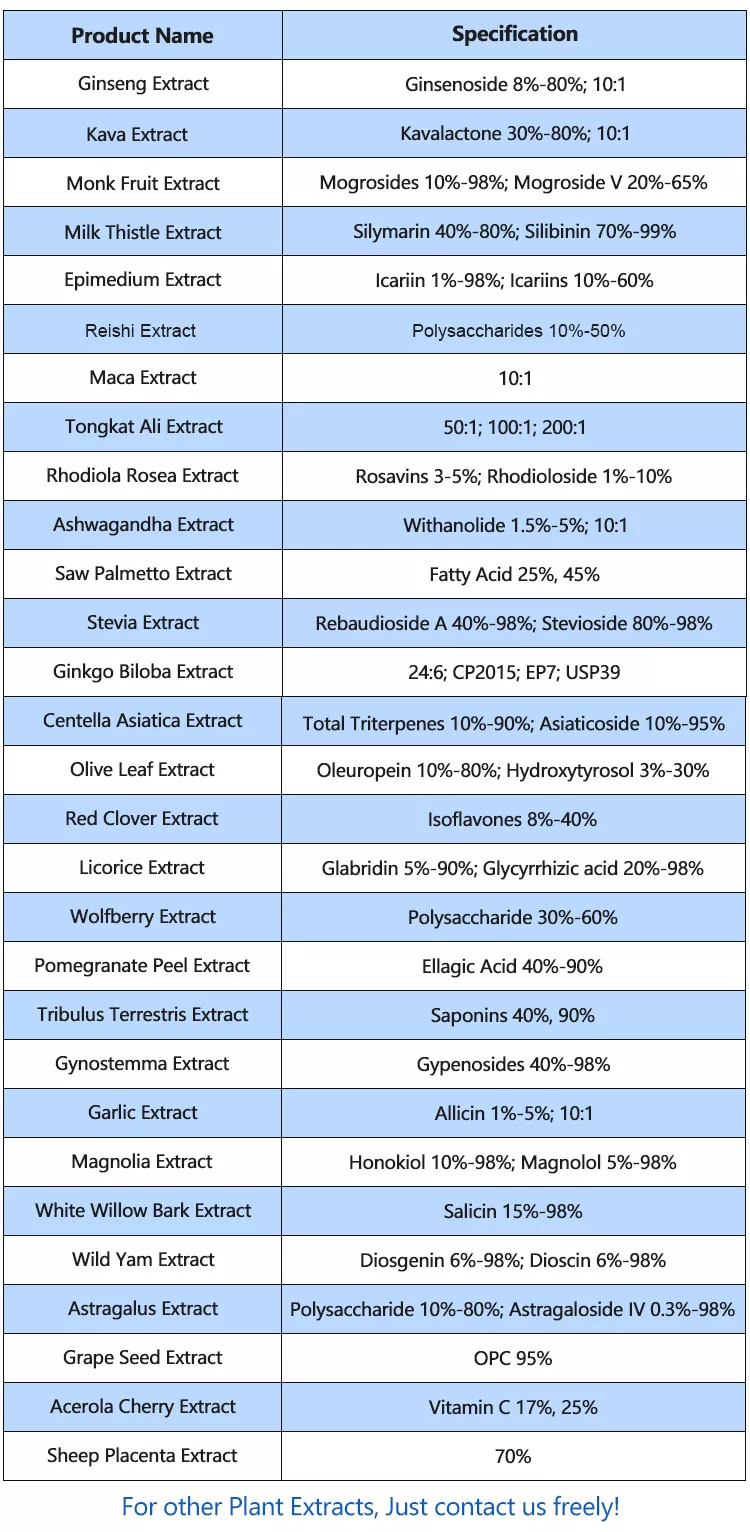
Ginseng Extract comes from the root of the ginseng plant, specifically the Panax ginseng species. Ginseng is a perennial plant that belongs to the Araliaceae family and is native to Eastern Asia, including countries like China, Korea, and Russia. It has been used for centuries in traditional medicine due to its potential health benefits.
The root of the ginseng plant is the part that is typically used for its medicinal properties. After harvesting the root, it is often processed and dried before being ground into a fine powder, which is then used as a dietary supplement or herbal remedy. Ginseng is believed to contain various bioactive compounds, such as ginsenosides, that are thought to contribute to its potential health-promoting effects, including increased energy, improved cognitive function, and enhanced immune system support.
Ginseng Extract is used in various forms, including capsules, teas, tonics, and even added to foods and beverages for its potential health benefits. It’s important to note that while ginseng is considered to have several potential health benefits, its effects can vary depending on factors such as the specific species of ginseng, the processing method, and individual differences in response. As with any herbal supplement, it’s a good idea to consult with a healthcare professional before incorporating ginseng powder into your diet, especially if you have any pre-existing health conditions or are taking medications.
The extraction of Ginseng Powder process
The extraction of Ginseng Extract typically involves the separation of the bioactive compounds from the ginseng root using solvents. The process is designed to obtain concentrated extracts that can be used for various purposes, such as herbal supplements, traditional medicine, or cosmetic products. Here’s a general overview of the extraction process:
Materials and Equipment:
1.Ginseng Roots: High-quality ginseng roots are harvested and dried.
2.Solvent: Ethanol, water, or a combination of both are commonly used solvents for ginseng extraction.
3.Grinder: A machine is used to grind the dried ginseng roots into a fine powder.
4.Extraction Equipment: This includes devices like Soxhlet extractors, maceration systems, or modern methods like ultrasonic or supercritical fluid extraction systems.
5.Filtration Equipment: Filtration tools are used to remove solid particles from the extract.
Extraction Process:
1.Preparation: Dried ginseng roots are cleaned to remove dirt and foreign particles. They are then finely ground into a powder using a grinder. The finer the powder, the larger the surface area available for extraction.
2.Choice of Solvent: The choice of solvent depends on the target compounds to be extracted. Ethanol is often used to extract a broad spectrum of ginsenosides (bioactive compounds in ginseng), while water is suitable for extracting polysaccharides.
3.Extraction Methods:
- Maceration: The Ginseng Extract is mixed with the chosen solvent and allowed to sit for a certain period, during which the solvent gradually extracts the compounds.
- Soxhlet Extraction: This method involves continuous solvent circulation through the powder. It’s suitable for extracting heat-sensitive compounds.
- Ultrasonic Extraction: Ultrasonic waves create cavitation bubbles that disrupt cell walls, aiding in the release of compounds into the solvent.
- Supercritical Fluid Extraction: Carbon dioxide in its supercritical state is used as a solvent. This method is highly efficient and can extract a wide range of compounds.
4.Extraction Duration: The extraction time can vary from a few hours to several days, depending on the chosen method and desired compound concentration.
5.Filtration: Once the extraction is complete, the mixture is filtered to remove any remaining solid particles from the extract. This results in a liquid extract.
6.Concentration: The liquid extract is often concentrated to increase the potency of the active compounds. This can be done through methods like rotary evaporation or freeze-drying.
7.Quality Control: The extracted Ginseng Extract undergoes quality control testing to determine the concentration of key compounds and ensure product consistency and safety.
8.Packaging: The final ginseng extract is typically packaged in appropriate containers, such as bottles or capsules, for distribution and consumption.
It’s important to note that the extraction process can vary based on the specific ginseng species, intended use of the extract, and available equipment. Additionally, proper attention should be given to quality control and safety measures throughout the extraction process to ensure the final product’s effectiveness and consumer safety.
