L-Arginine is an amino acid, which is one of the building blocks of proteins in the body. It is classified as a semi-essential or conditionally essential amino acid, meaning that under normal circumstances, the body can synthesize it from other amino acids. However, in certain situations, such as during periods of rapid growth, illness, or stress, the body may not produce enough L-Arginine, making it necessary to obtain it through the diet or supplements.
L-Arginine plays several important roles in the body, including:
Nitric Oxide (NO) Production: L-Arginine is a precursor to nitric oxide, a molecule that helps relax and dilate blood vessels. This dilation of blood vessels can improve blood flow and circulation, which is important for cardiovascular health.
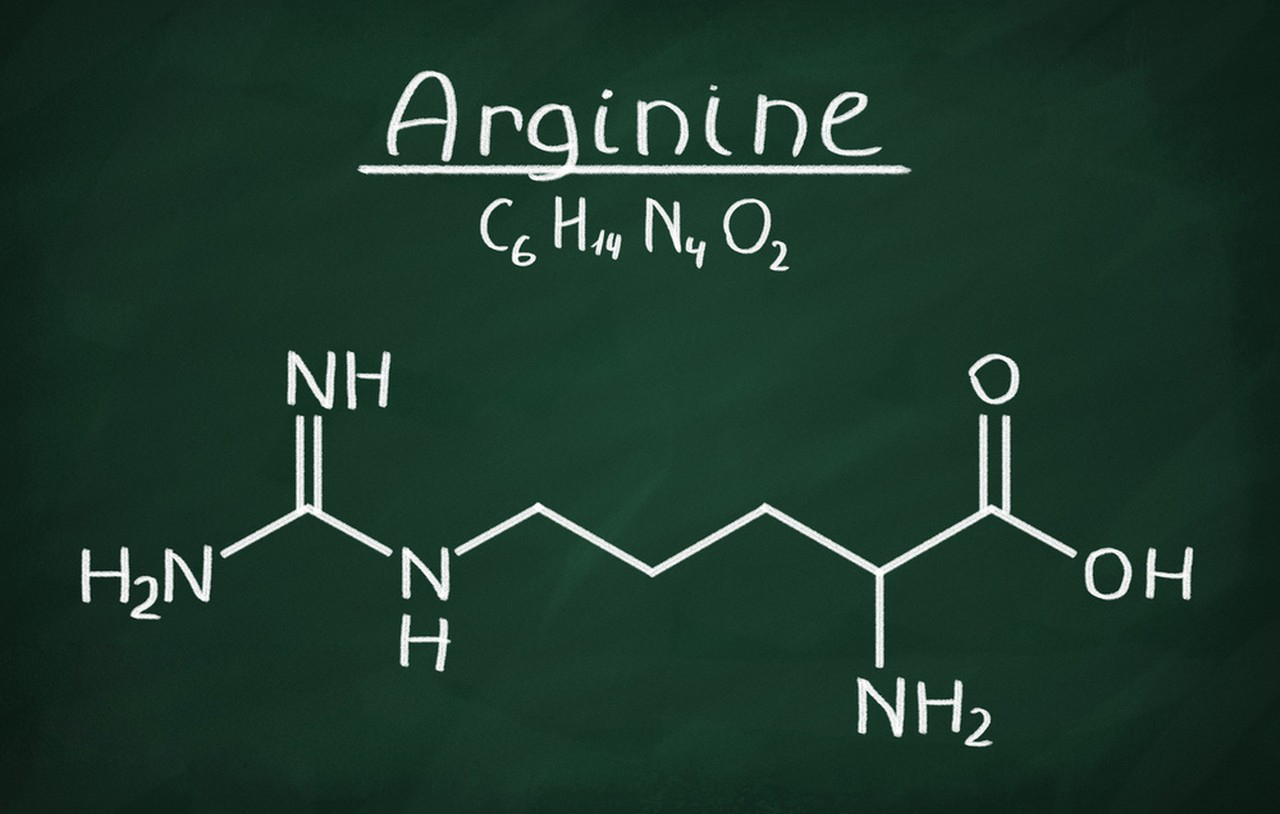
Wound Healing: L-Arginine is involved in the production of collagen and other compounds necessary for wound healing and tissue repair.
Immune Function: It plays a role in supporting the immune system by aiding in the production of immune cells and promoting the release of hormones like insulin and growth hormone.
Detoxification: L-Arginine is involved in the removal of ammonia from the body, which is a waste product of protein metabolism.
Hormone Regulation: It is essential for the production of certain hormones, such as insulin and glucagon.
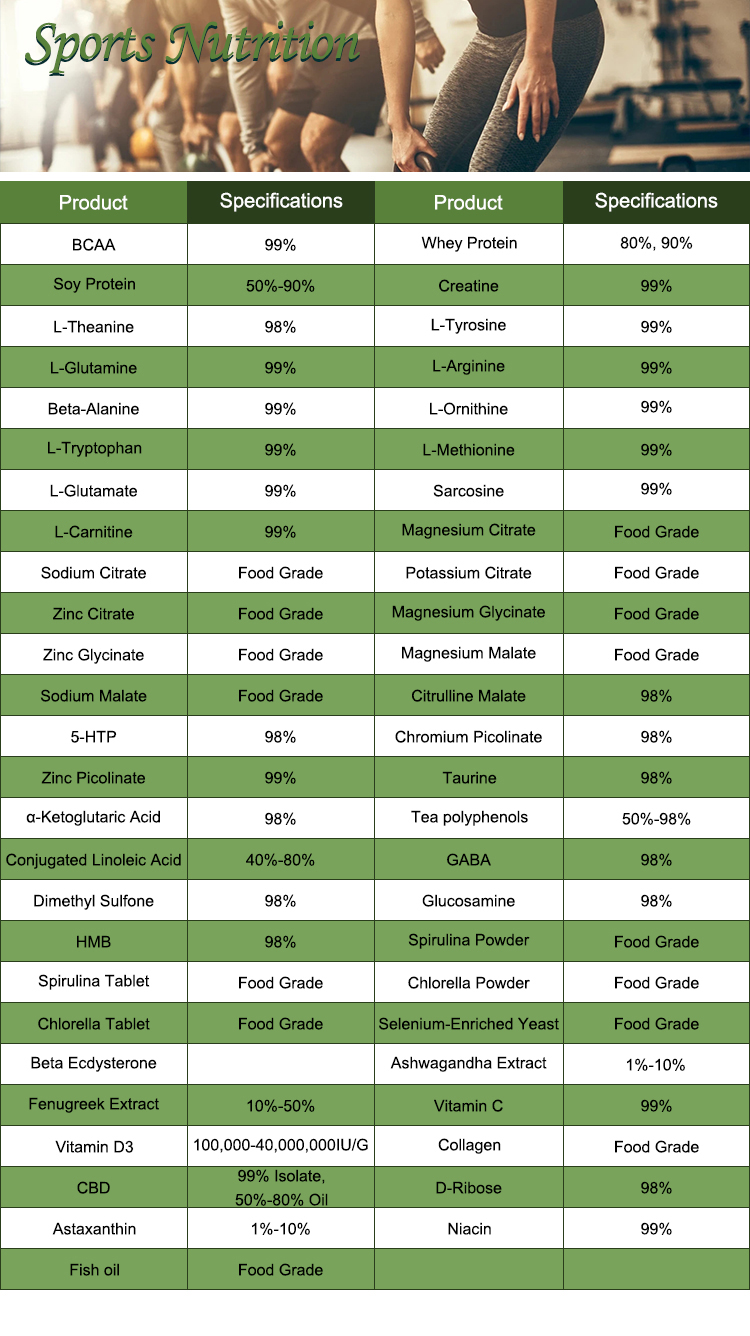
Arginine is found in various foods, including red meat, poultry, fish, dairy products, nuts, and seeds. It is also available in supplement form, often marketed for its potential health benefits, such as improving athletic performance, promoting heart health, and enhancing sexual function. However, the scientific evidence supporting many of these claims is mixed, and it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before taking L-Arginine supplements, especially if you have underlying medical conditions or are taking medications, as it can interact with certain drugs.
How to use L-Arginine?
L-Arginine is an amino acid that plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including the production of nitric oxide, which helps relax blood vessels and improve blood flow. As a dietary supplement, L-arginine is sometimes used to support various health goals, such as improving cardiovascular health, enhancing exercise performance, or managing certain medical conditions. Here are some guidelines on how to use L-arginine:
Consult with a Healthcare Professional: Before starting any new supplement regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian. They can provide personalized advice based on your specific needs and medical history.
Determine Your Dosage: L-arginine is available in various forms, including capsules, tablets, powders, and liquids. Dosage recommendations can vary widely based on the intended use and individual factors. A common dosage for general health support ranges from 2,000 to 6,000 milligrams (2 to 6 grams) per day. However, dosages can be higher for specific purposes, such as athletic performance or medical conditions.
Take it as Directed: Follow the instructions on the product label or the guidance provided by your healthcare professional. Some people prefer to split their daily dosage into multiple servings throughout the day to maintain a consistent level of L-arginine in their system.
Consider Timing: L-arginine is often taken on an empty stomach to improve absorption. However, some individuals may experience gastrointestinal discomfort when taking it this way. If that happens, you can take it with a small meal or as directed by your healthcare provider.
Be Patient: L-arginine may take some time to provide noticeable benefits, and the effects can vary from person to person. It’s not a quick-fix solution, so be patient and consistent with your supplementation.
Monitor for Side Effects: While L-arginine is generally considered safe for most people when used as directed, some individuals may experience side effects such as stomach upset, diarrhea, or allergies. If you experience any adverse effects, discontinue use and consult your healthcare professional.
Know Potential Interactions: L-arginine may interact with certain medications, particularly those that affect blood pressure, blood thinning, or diabetes management. Discuss potential interactions with your healthcare provider if you’re taking any medications.
Consider Your Health Goals: L-arginine is used for various purposes, so it’s essential to have a clear
understanding of your health goals when using it. Whether you’re using it for heart health, exercise performance, or another purpose, make sure your dosage and usage align with those goals.
Maintain a Balanced Diet: While supplementation can provide additional L-arginine, it’s also essential to consume a balanced diet that includes foods rich in protein, as L-arginine is naturally found in many protein-rich foods like meat, fish, and dairy products.
Regularly Review Your Usage: Periodically reassess your use of L-arginine with your healthcare provider to ensure it aligns with your changing health needs and goals.
Remember that individual responses to L-arginine can vary, so it’s crucial to work closely with a healthcare professional to determine the right dosage and usage for your specific situation. Additionally, dietary supplements should complement a healthy lifestyle and not replace it, so continue to prioritize a balanced diet, regular exercise, and other aspects of overall well-being.
